GLOSSARY OF SCIENTIFIC TERMS
- absolute zero. The lowest theoretical temperature (0K = -273.16°C) where all molecular activity ceases.
- acceleration. Rate of change of velocity.
- acid. A compound that yields hydrogen ions (H+) when in aqueous solution. Acids have a sour taste and turn blue litmus red.
- activation energy. The energy required to initiate a chemical reaction.
- adiabatic system. A system that neither gains or looses heat.
- alcohol. Organic compound used in gums, resins, dyes and perfumes. Fermentation produces ethanol not alcohol.
- alkali. A base that is soluble in water.
- allele. Gene variant.
- allotrope. Element with more than one natural form.
- alloy. A substance formed by the combination of two or more elements, at least one of which must be a metal.
- amino acids. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen compounds the composition of which are determined by genes.
- anion. A negative ion.
- atomic number. The number of protons in an atom..
- atomic symbol. The letters representing each of the elements.
- atomic weight. The average weight of an atom.
- atoms. Composite particles of protons, neutrons and electrons. The smallest part of a substance that can take part in a chemical reaction. Click here for more information.
- baryon. A three quark hadron. The most common baryons are protons and neutrons.
- base. A compound that yields hydroxide (OH- ) ions when in aqueous solution. Bases have a bitter taste, feel greasy and turn red litmus blue.
- biosynthesis. The production of cellular material.
- boiling point. The temperature at which a liquid turns to a vapour.
- bond. A chemical link between atoms.
- capacitance. The ability to store an electric charge.
- carbohydrates. The major energy source within plants and animals: sugars, starches and glucose polymers.
- carbon. The basic element in all organic compounds.
- catalyst. A substance that reduces the activation energy of a reaction.
- cation. A positive ion.
- cell. The smallest independent part of an organism.
- chain reaction. Polymerisation initiated by the bonding of a free radical with a monomer.
- charge. The amount of unbalanced electricity in a system. Either positive or negative.
- chemical equation. The mathematical representation of a chemical reaction.
- chemical (empirical) formula. The ratio of elements in a substance. For example: the chemical formula of common salt is NaCl, sodium and chlorine in a ratio of 1:1.
- chemical reaction. The transformation of substances by the rearrangement of their atoms.
- chromosomes. DNAmolecules that contain the set of instructions required to build and maintain cells.
- compound. A substance containing more than one element.
- conduction. Heat or electricity transfer through molecular interaction, eg: heat passing along a metal bar.
- convection. Heat transfer through the movement of a fluid, eg: warm air rising.
- coulomb attraction. Electrostatic attraction between bodies of opposite charge
- covalent bond. A bond formed between atoms that share electrons.
- crystal. Solid substance with a regular geometirc arrangement of atoms.
- cytosol. Jelly-like substance within cells.
- density. The mass per unit volume in a substance.
- diffraction. The deviation in the path of a wave that encounters the edge of an obstacle.
- diffusion. The random movement of molecules within a fluid.
- DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid. Twisted helical polymer chains. See chromosomes.
- elasticity. The ability of a body to regain its original shape after deformation.
- electric current. A flow of electrons through a conductor, the size of the current is proportional to the rate of electron flow.
- electrons. Negatively charged atomic particles.
- electromagnetic waves. Waves with both an electric and magnetic component. They are: radio, micro, infra-red, visible light, ultraviolet, X and gamma rays.
- electrolyte. An ion solution that is an electrical conductior.
- element. A substance composed of atoms all with the same atomic number. A substance that cannot be split chemically into smaller substances.
- endothermic reaction. A reaction in which heat is absorbed ie: melting or boiling.
- energy. The capacity to do work. Work is done by transferring energy from one form to another. For example the chemical energy in a fuel is converted to thermal energy as it burns. See also Laws of Thermodynamics.
- entropy. The state of disorder in a thermodynamic system: the more energy the higher the entropy.
- enzymes. Biological catalysts, proteins that control specific processes within the body.
- equilibrium. A stable situation in which products and reactants are balanced.
- evaporation. The change of state of a substance from a liquid to a gas below its boiling point.
- evolution. Natural selection, the survival of the fittest, is the driving force behind evolution and is measured by a species viability and fecundity. Governed by Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection:
- 1. The distinguishing features (characters) of an organism may affect it fitness.
- 2. The design of an species (its morphology) differs within a population and may improve its fitness.
- 3. An organism may be susceptible to a lack of vital resources, predation and disease reducing its fitness.
- 4. The characters that improve fitness must be inherited. Individuals that inherit these characters will survive at the expense of those who do not.
- 5. Mutation is essential for evolution: the inheritance of non-standard genes that improve fitness.
- Note: Fitness is the ability to survive and reproduce, not necessarily a measure of physical fitness.
- exothermic reaction. A reaction from which heat is lost eg: combustion.
- fats. Molecules of fatty acids or glycerol. Used as a food store, insulation and for shock absorption.
- fecundity. The ability to breed.
- field. A region in space that is defined by a vector function. Common fields are: gravitational, electric and magnetic.
- fission. Splitting the nucleus of an atom into smaller units.
- fluid. A liquid or gas.
- force. An action (transfer of energy) that will accelerate a body in the direction of the applied force. See Newtons Laws of Motion.
- free radical. A highly reactive molecule used to start the production of a polymer chain.
- frequency. The rate as which periodic motion repeats itself.
- friction. The interaction between surfaces: a measure of the resistance felt when sliding one body over another.
- fundamental particles. Those particles that are not known to contain any smaller components: leptons, quarks and gauge bosons.
- fusion. 1. Change of state of a substance from a solid to a liquid. 2. The joining together of two atomic nuclei.
- gametes. Sex cells (spermatozoa or ova) that carry the genes donated by each parent.
- gauge bosons. Particles that mediate the transfer of energy between other particles: protons, gravitons, W and Z particles.
- gene. A unit of inheritance. A section of DNA. comprising a sequence of four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine.
- genome. The collective noun for a set of genes. The human genome contains 100 000 genes.
- gravity. The attraction that all bodies have for one another.
- hadrons. Quark composites: mesons and baryons. Protons and neutrons are the most common hadrons.
- half-life. The time taken for the level of radioactivity in an element to halve.
- halogen. Highly reactive gases forming group 7 of the periodic table.
- heat. The internal energy of a body (substance).
- hydrocarbon. Compounds containing only hydrogen and carbon atoms.
- ideal gas. One which obeys the ideal gas law. At low pressures, real gases behave like ideas gases.
- inertia. Tendency of a body to remain at rest or move in straight line.
- inheritance. The features of an organism are determined by a set of chromosomes. These originate in the parents and are passed on to an offspring during fertilisation. It follows then that since chromosomes are inherited, all the features of an organism must be inherited.
- ion. Atom with an unbalanced electrical charge caused by the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
- ionic bond. An bond formed by the electro-magnetic attraction between ions of opposite charge.
- isomer. Chemical compounds with the same composition but different shapes.
- isomeric structure. The shape of a molecule. The isomeric structure is determined by the order in which the atoms are bonded together.
- isotope. An element that has more or less neutrons than normal. Many isotopes are radioactive.
- kinetic energy. The energy possessed by a body in motion.
- latent heat. The amount of energy required to change a solid to a liquid or liquid to a gas.
- Laws of Themodynamics.
- 1. The amount of energy in the universe is fixed. It cannot be created or destroyed only changed from one state to another.
- 2. Heat cannot pass from a cold to a hot body. The opposite condition where heat always flows from a hot to a cold body is valid for the whole universe.
- lens. Light modifier. Convex lenses focus and concave lens diffuse light waves.
- leptons. Fundamental particles that are relatively non-reactive and capable of an independent existence: electrons, muons, tau particles and neutrinos.
- light. The visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. White light is a combination of all the above colours.
- magnet. A body which produces a magnetic field. All magnets are di-pole and follow the rule that like poles repel and unlike poles attract.
- mass. The quantity of matter in a body.
- mesons. Two quarkhadrons, the product of radioactive decay.
- metals. Elements characterised by their opacity, malleability and thermal and electrical conductivity.
- mitochondria. Organelles that convert glucose into energy.
- molecular formula. The number and types of atom in a molecule. For example the molecular formula of methane is CH4, one atom of carbon and four atoms of hydrogen.
- molecule. A group of atoms bonded together. It is the smallest part of a substance that retains the chemical properties of the whole.
- moment. A rotating effect. See torque.
- momentum. The product of mass times velocity. Momentum is conserved in any system of particles.
- monomers. Small molecules that link together to form a polymer.
- neutralization. A reaction in which the characteristics of an acid or base disappear.
- neutrons. Particles with zero charge forming part of an atomic nuclei. 3 quarkhadrons.
- Newtons Laws of Motion. Classical laws which enable the prediction of the path of any object from a grain of sand to entire galaxies:
- 1. A body will remain at rest or move with a constant velocity unless acted upon by an outside force.
- 2. The acceleration of a body is proportional to the applied force. This is expressed by the universal formula: Force = mass × acceleration.
- 3. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
- noble gases. Elements with zero valency. They form group 0 in the periodic table and are non-reactive.
- nucleus. 1. Organelle containing the chromosomes. 2. That part of an atom containing the protons and neutrons.
- organelles. Specialized organs within cells.
- organic compounds. Substances that contain Carbon.
- ozone. An isotope of oxygen that blocks ultra-violet radiation. Normally found in the stratosphere.
- pH Scale. The strength of acids and bases. Pure water has a pH value of 7, acids have a lower value and bases higher.
- phase changes. Freezing or boiling.
- photo-synthesis. The conversion of water and carbon-dioxide by plants into glucose and oxygen. Light is used as an energy source.
- photons. Fundamental quantum particles. It is the interaction of photons with other particles that drives the universe.
- polymerisation. The repetitive bonding of small molecules (monomers) to produce large molecules (polymers).
- polymers. Long chain molecules such as PVC, nylon or DNA produced by the polymerisation of monomers.
- potential difference. The voltage difference between two points. Electricity flows from a high to low level of potential.
- potential energy. Amount of useable energy within a body at rest.
- power. Amount of work done per second.
- products. The substances produced in a chemical reaction.
- proteins. Amino acid polymers with specific biological functions, especially the growth, regeneration and repair of cells.
- protons. Positively charged particles forming part of atomic nuclei. 3 quarkhadrons.
- quantum theory. The theory that energy can only be absorbed or radiated in discrete values or quanta. All particles are subject to quantum theory. Click here to find out more.
- quarks. Fundamental particles, incapable of independent existence, that combine to form particles such as protons and neutrons.
- radiation. 1. Transfer of heat between bodies without a change in the temperature of the intervening medium. 2. Any release of energy from its source.
- radioactivity. The spontaneous release of energy from atomic nuclei.
- reactants. The substances that take part in a chemical reaction.
- refraction. The deflection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another, eg through a lens.
- relative atomic mass (RAM). The mass of an atom relative to one atom of carbon. Carbon has a RAM of 12.
- relativity. The relative values of time, motion, mass and energy of a body in motion. Click here for more information
- reproduction. Reproduction is the process by which a new organism is produced. The first stage in the production of any organism is the fertilisation of an ova by spermatozoa (or spores on the case of plants). Fertilisation produces a single cell called a zygote which contains all the information required to build the adult organism. The progression (growth) from zygote to adult is achieved through cell division.
- resistance. Opposition to current flow in a conductor.
- resonance. A state where the natural frequency of a body equals an applied frequency.
- respiration. The production of energy by the oxidisation of glucose.
- scalar. A quantity that is defined by its magnitude only (ie energy, temperature).
- simple harmonic motion. A repeating motion about a central equilibrium point (pendulum, weighted spring).
- special relativity. The observable effects on a body in motion. As velocity increases, time slows down, mass increases and lengths contract.
- speciation. A group of organisms that are able to interbreed all belong to the same species. It follows then that organisms that are unable to interbreed belong to separate species.
- specific heat. The heat capacity of a body.
- standard model. The organization and relationships between fundamental particles. Click here for more information.
- strain. The deformation of a body under an applied load.
- stress. The measure of the force acting on a body.
- temperature. How hot one body is when compared to another.
- torque. The tendency of a body to rotate under an applied force..
- uncertainty. It is impossible to know exactly where something is and where it is going. This is a fundamental law of nature has a major effect on quantum theory.
- valency. A measure of the reactivity of an element.
- vector. A quantity that is determined by its magnitude and direction: forces and fields (see scalar).
- velocity. The rate of change of distance with respect to time.
- viability. The ability to survive to adulthood.
- viscosity. The internal friction of a fluid, thick fluids have a high viscosity and thin fluids low.
- weight. The gravitational force exerted on a mass.
- work. The amount of energy transferred to a system.
- zygote. A fertilised egg, the fusion of a male and female gamete.
SCIENTIFIC DIVISIONS
PHYSICS
The study of the relationships between energy and matter. The two major divisions are: Newtonian (classical) physics and modern (particle) physics.
Prior to 1687 it was believed that the natural state of a body was at rest. This theory was blown apart by Newton in his book Principa Mathematica in which it was demonstrated that the natural state of a body was in motion (See Newtons Laws of Motion). So important was this theory that it became the basis of all future physics research.
The cornerstones of modern physics are Quantum Theory and Relativity. They are based on the theories and concepts developed since 1900 and affect all aspects of scientific research. Much of modern physics is involved with the properties and behaviour of sub-atomic particles.
CHEMISTRY
Chemistry is the scientific study of the composition and changes in substances. The main divisions are: biochemistry (living organisms), organic chemistry (carbon and its compounds) and inorganic chemistry (elements and compounds other than carbon).
The chemical composition of any substance is defined by the numbers of its constituent atoms, their distribution and the bonds between them. All substances can be represented by a chemical or molecular formula.
In a chemical reaction, two or more reactants are transformed into a number of products as the existing chemical bonds are broken and new ones formed. A bond is a chemical link between atoms. The main types of bonds are covalent and ionic.
BIOLOGY
Biology is the study of living organisms. Sometimes called the life sciences, biology is concerned with whole populations, single organisms, organs, cells and the biochemical processes that control life.
THE ELEMENTS
Symbol | Name | Atomic Number | Relative Atomic Mass |
| Ac | Actinium | 89 | 227.03 |
| Ag | Silver | 47 | 107.87 |
| Al | Aluminium | 13 | 26.98 |
| Am | Americium | 95 | 243.06 |
| Ar | Argon | 18 | 39.95 |
| As | Arsenic | 33 | 74.92 |
| At | Astatine | 85 | 210 |
| Au | Gold | 79 | 196.97 |
| B | Boron | 5 | 10.81 |
| Ba | Barium | 56 | 137.34 |
| Be | Beryllium | 4 | 9.01 |
| Bh | Bohrium | 107 | 264.12 |
| Bi | Bismuth | 83 | 208.98 |
| Bk | Berkelium | 97 | 247.07 |
| Br | Bromine | 35 | 79.9 |
| C | Carbon | 6 | 12.01 |
| Ca | Calcium | 20 | 40.08 |
| Cd | Cadmium | 48 | 112.40 |
| Ce | Cerium | 58 | 140.12 |
| Cf | Californium | 98 | 251.08 |
| Cl | Chlorine | 17 | 35.45 |
| Cm | Curium | 96 | 247.07 |
| Co | Cobalt | 27 | 58.93 |
| Cr | Chromium | 24 | 52 |
| Cs | Caesium | 55 | 132.91 |
| Cu | Copper | 29 | 63.55 |
| Db | Dubrium | 104 | 261.11 |
| Dy | Dysprosium | 66 | 162.50 |
| Er | Erbium | 68 | 167.26 |
| Es | Einsteinium | 99 | 252.09 |
| Eu | Europium | 63 | 151.96 |
| F | Fluorine | 9 | 19 |
| Fe | Iron | 26 | 55.85 |
| Fm | Fermium | 100 | 257.1 |
| Fr | Francium | 87 | 223.02 |
| Ga | Gallium | 31 | 69.72 |
| Gd | Gadolinium | 64 | 157.25 |
| Ge | Germanium | 32 | 72.59 |
| H | Hydrogen | 1 | 1.01 |
| He | Helium | 2 | 4 |
| Hf | Hafnium | 72 | 178.49 |
| Hg | Mercury | 80 | 200.59 |
| Hn | Hahnium | 108 | 265.13 |
| Ho | Holmium | 67 | 164.93 |
| I | Iodine | 53 | 126.90 |
| In | Indium | 49 | 114.82 |
| Ir | Iridium | 77 | 192.22 |
| Jl | Joliolium | 105 | 262.11 |
| K | Potassium | 19 | 39.10 |
| Kr | Krypton | 36 | 83.80 |
| La | Lanthanum | 57 | 138.91 |
| Li | Lithium | 3 | 6.94 |
| Lr | Lawrencium | 103 | 262.11 |
| Lu | Lutetium | 71 | 174.97 |
| Md | Mendelevium | 101 | 258.1 |
| Mg | Magnesium | 12 | 24.31 |
| Mn | Manganese | 25 | 54.94 |
| Mo | Molybdenum | 42 | 95.94 |
| Mt | Meitneriuum | 109 | 268 |
| N | Nitrogen | 7 | 14.01 |
| Na | Sodium | 11 | 22.99 |
| Nb | Niobium | 41 | 92.91 |
| Nd | Neodymium | 60 | 144.24 |
| Ne | Neon | 10 | 20.18 |
| Ni | Nickel | 28 | 58.71 |
| No | Nobelium | 102 | 259.10 |
| Np | Neptunium | 93 | 237.05 |
| O | Oxygen | 8 | 16 |
| Os | Osmium | 76 | 190.2 |
| P | Phosphorus | 15 | 30.97 |
| Pa | Protactinium | 91 | 231.04 |
| Pb | Lead | 82 | 207.2 |
| Pd | Palladium | 46 | 106.4 |
| Pm | Promethium | 61 | 144.91 |
| Po | Polonium | 84 | 208.98 |
| Pr | Praseodymium | 59 | 140.91 |
| Pt | Platinum | 78 | 195.09 |
| Pu | Plutonium | 94 | 244.06 |
| Ra | Radium | 88 | 226.03 |
| Rb | Rubidium | 37 | 85.47 |
| Re | Rhenium | 75 | 186.2 |
| Rf | Rutherfordium | 106 | 266.12 |
| Rh | Rhodium | 45 | 102.91 |
| Rn | Radon | 86 | 222.02 |
| Ru | Ruthenium | 44 | 101.07 |
| S | Sulphur | 16 | 32.06 |
| Sb | Antimony | 51 | 121.75 |
| Sc | Scandium | 21 | 44.96 |
| Se | Selenium | 34 | 78.96 |
| Si | Silicon | 14 | 28.09 |
| Sm | Samarium | 62 | 150.35 |
| Sn | Tin | 50 | 118.69 |
| Sr | Strontium | 38 | 87.62 |
| Ta | Tantalum | 73 | 180.95 |
| Tb | Terbium | 65 | 158.93 |
| Tc | Technetium | 43 | 97.91 |
| Te | Tellurium | 52 | 127.60 |
| Th | Thorium | 90 | 232.04 |
| Ti | Titanium | 22 | 47.90 |
| Tl | Thallium | 81 | 204.37 |
| Tm | Thulium | 69 | 168.93 |
| U | Uranium | 92 | 238.03 |
| Uun | Ununnilium | 110 | 271 |
| Uuu | Unununium | 111 | 272 |
| V | Vanadium | 23 | 50.94 |
| W | Tungsten | 74 | 183.85 |
| Xe | Xenon | 54 | 131.30 |
| Y | Yttrium | 39 | 88.91 |
| Yb | Ytterbium | 70 | 173.04 |
| Zn | Zinc | 30 | 65.37 |
| Zr | Zirconium | 409 | 91.22 |
THE 'OLOGIES'
Whilst most of the true sciences are included in the following list, there are some 'ologies' whose claim to scientific status is questionable. The addition of the suffix -ology to a subject does not necessarily make it a science.
The suffix -logy refers to the investigative sciences and -graphy refers to the descriptive sciences. The root sciences, where applicable, are shown in brackets.
- anatomy. Structure of the parts of the body.
- anthropo-. Man.
- anthropology. Natural history of man.
- apiology. Bees (biology)
- archaeology. Material remains of the past.
- architecture. Design and erection of buildings.
- astro-. Greek. star.
- astrology. Prediction through celestial observation.
- astronautics. Space flight.
- astronomy. Celestial bodies excluding the Earth.
- astrophysics. Physical and chemical properties of celestial bodies.
- bacteriology. Bacteria.
- ballistics. Flight patterns of projectiles.
- biochemistry. Chemical composition and changes in living organisms.
- biology. Living organisms.
- bionomics. See ecology.
- biophysics. Physical characteristics of biological processes.
- botany. Plants (biology).
- cartography. Maps and Mapmaking.
- cetology. Whates (biology).
- chemistry. Composition, properties and changes of substances.
- climatology. The climate (meteorology)
- cladistics. Classification of animals from genetic information.
- conchology. Seahells
- cosmology. Origin and nature of the universe (astronomy).
- criminology. Crimes.
- cryogenics. Very low temperatures (physics).
- cryptography. Codes and ciphers.
- cytogenetics. Heredity and variation in cells.
- cytology. Plant and animal cells.
- dendrology. Trees (biology).
- demography. Size and distribution of human populations.
- desmology. Branch of Medicene dealing with ligaments and sinews.
- dynamics. Forces acting on moving objects (mechanics).
- ecology. Relationships between life and its natural habitats.
- embryology. Changes in plants and animals as embryos.
- entomology. Insects.
- ergonomics. Relationship between worker and environment.
- eschatology. Death and the afterlife.
- ethnology. Origins and characteristics of individual races and peoples (anthropology).
- ethology. Natural behaviour of animals.
- etiology. Causes of disease.
- etymology. Source and development of words (linguistics).
- genealogy. Evolution and descent of a species or family.
- genetics. Heredity and variation in organisms.
- geochronology. Relationship of time to Earth's history.
- geodesy. The position of features on the Earth's surface (geography).
- geography. Natural features of the Earth's surface.
- geology. Structure of the earth.
- geomorphology. Origin and changes of topographical features (geology).
- geophysics. Physical properties of the Earth: meteorology, oceanography and seismology.
- geostatics. Balance of forces in the Earth (physics).
- graphology. Handwriting.
- gynaecology. Diseases of the female reproductive system.
- haematology. Blood and its diseases (pathology).
- herpetology. Reptiles.
- hippology. Horses.
- histology. Tissues.
- hydrography. Surveying and mapping of the rivers and seas.
- hydrokinetics. Fluids in motion.
- hydrology. Distribution and use of the earth's water.
- hydrostatics. Fluids at rest.
- ichthyology. Fishes.
- ideology. Ideas and concepts.
- kinematics. Motion of bodies without reference to mass or force (mechanics).
- kinetics. See dynamics.
- linguistics. Language.
- lithology. Physical characteristics of rocks (geology).
- mammology. Mammals
- mathematics. The relationships between number, quantity, size and shape.
- mechanics. Bodies in motion: dynamics, kinematics and statics (physics).
- medicine. Preventing, diagnosing and curing disease.
- metallurgy. Extraction, refining and alloying of metals.
- metallography. Structure of metals and alloys.
- meteorology. The atmosphere, especially the weather (geophysiscs).
- metrology. Measurement.
- mineralogy. Composition and characteristics of minerals (geology).
- morphology. 1. Form and structure of organisms (biology). 2. Form and structure of words (linguistics).
- mycology. Fungi (botany).
- myrmecology. Ants (biology).
- mythology. Interpretation of stories and myths.
- nephology. Clouds (meteorology).
- neurology. Nerves and the nervous system.
- oceanography. Oceans and seas (geology).
- odontology. Teeth (medicine).
- ontogeny. The sequence of events in the development of an organism.
- opthalmology. Eyes.
- ornithology. Birds
- orography. Mountains (geography).
- osteology. Bones (medicine).
- otology. Ears (medicine).
- palaeography. Ancient writings.
- palaeontology. Determination of the past from fossils.
- pathology. Causes and results of disease (medicine).
- pedology. Soil (biology).
- petrography. Description and classification of rocks (geology).
- petrology. Composition, origin and formation of rocks (geology).
- pharmacology. Drugs and their effect on the body.
- philology. History of language (linguistics).
- phonetics. Vocal sounds (linguistics).
- phonology. Sounds within a language (linguistics).
- philology. Historical language.
- philosophy. Explanation of nature and science by rational argument.
- physics. Relationship between matter and energy.
- physiology. Functions of organisms and their parts.
- phylogeny. Origins of plants (botany).
- psychology. Human and animal behaviour.
- seismology. Earthquakes (geology).
- semantics. Meaning of language (linguistics).
- semiology. Symptoms of disease.
- sociobiology. Social behaviour in humans and animals.
- sociology. Society.
- speleology. Caves.
- statics. Forces in equilibrium (mechanics).
- statistics. Collection and interpretation of quantative data.
- taxonomy. Classification of animals and plants (biology).
- technology. Practical application of the arts and sciences.
- thanatology. Death.
- theology. Religion and the nature of divinity.
- thermodynamics. The relationships between different forms of energy.
- topography. Surface features of a region.
- toxicology. Poisons.
- uranography. Mapping the stars and galaxies (astronomy).
- virology. Viral diseases.
- vucanology. Volcanos.
- zoology. Animals.
THEORIES OF MOTION
ARISTOTLE
Aristotle developed the first theory of motion (among other things) and got it wrong. Unfortunately it is the theory that most people use to describe how things move.
The theory stated that everything is in a state of rest until you give it a push. Seems reasonable: you are sitting down and not moving. And until your muscles give you a push you will not start moving. It was a pretty good theory and stood the test of time until the 17th Century when it was buggered up by the all new, never before published Newton's Theory of Motion.
NEWTON'S THEORY OF MOTION
Newton's Theory of Motion says simply that everything is stationary or keeps on going until you give it a push.
It works like this: Imagine a ball bearing rolling along a very long (infinite) table. If we ignore friction and air resistance, the ball bearing will continue to roll forever until you stop it.
OR
Imagine an astronaut floating in space. He will continue to float along until he whacks into something. But what (I hear you cry) about me sitting in front of my computer. Well if the ground was not underneath you would fall towards the centre of the Earth - it is the ground that stops you moving. Why do you fall to the centre of the Earth? Newton solved this puzzle as well - he worked out that everything is attracted to everything else - gravity is what glues the Universe together. It is what keeps us in motion.
Newton's Theory (once it became accepted) solved many of the problems confronting scientists. And it is still pretty good for calculating things such as how to catch a balll or get a man to the moon.
Unfortunately (again) is was not very good at explaining very small and very big motions: atomic structures and the shape of the universe itself.
This is where is gets a bit complicated. To solve these probelms two new theories were introduced: Quantum Theory for atoms and Relativity for the universe.
QUANTUM THEORY
Everything can be broken down into tiny packets or 'quanta' of energy. It's true, light is composed of photons, tiny blobs of quantum energy. We can even count them using special sensors, it is just that there are so many of them that all we see a continuous beam.
When a photon collides with an electron there is an increase in the quantum energy of the electron. This makes the electrons jump into the next quantum energy level - the size of the jump is dependant on the photon energy. Electron do not like being in this high energy or exicited state and will soon jump back to their original position and in doing so will emit a photon. This is happening all the time, it is the reason why this computer works, your heart pumps and the sun continues to shine.
This is really all you need to know about quantum theory: energy is absorbed or emitted by atoms in tiny packets which move on to the next atom and so on and so on forever.
To appreciate quantum theory, you need to suspend common sence. The quantum jump is a real jump, there is no movement from A to Z passing though all stations in between. There is nothing between A and Z in the quantum world.
The good news is that quantum effects can only be observed in atoms. The jumps are just too small to be noticed. Even so, every move you make is the result of billions of quantum jumps - the end result (for us) a seemingly smooth transition. Which is why we can use Newton's Theory of Motion in every day life (the fastest computer in the world could not calculate all the quantum changes needed to even blink your eyes).
RELATIVITY
Relativity was Einstein's great work. He worked out that because everything is attracted to everything else (gravity again) the motion of each of the bodies in the universe affects the motion of everything else.
Imagine a big metal ball plonked in the middle of a rubber sheet. The weight of the ball will stretch the rubber sheet, make a bit of a dip in the middle. If we put another ball on the sheet it will roll towards the dip. But if we whizz it around the dip it will orbit the heavy ball. Now obviously the Universe is not made of rubber but the same thing happens in space. Heavy things like stars 'distort' space attracting plants towards them and even bend light waves.
Einstein worked out that everything in the universe can be represented as an energy source. If you know the energy value of everything you can work out the distortion and therefore how it everything will move.
This is General Relativity and can be summaried as: matter tells space how to curve, space tells matter how to move
Special Relativity on the other hand is more to do with how we observe things. If you follow a cyclist you will see the pedals going up and down. Somebody else standing on the pavement will see the pedals going round and round. It is the position of the observer that determines what is observed.
The next stage is consider the speed of the motion. Without the mathematics, special Relativity can be summaried as: moving clocks slow down and moving bodies get smaller.
The good thing is, relativity has little effect on us here on Earth, we do not have enough energy or move fast enough. So Newton's Theory is good enough for most calculations.
COMPOSITION AND STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH
The Earth is the third planet in the solar system and is about 4600 billion years old. Over 65% of the surface is covered in water, the remainder broken up into five continental land masses.
The Earth rotates in an anti clockwise direction about an axis tilted over at 23.5o . The Earth is an oblate spheroid, flattened at the poles and bulging at equator.
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
crust. The outermost rock layer, divided into continental and oceanic crust. The continental crust is 25-90 km thick and is mostly granite and andesite. The oceanic crust is 6-11 km thick and mostly basalt.
mantle. The mantle stretches from the below the crust to 2900 km below the surface. The upper part is partially molten and the lower part is very dense. The main mantle rock is peridotite.
core. The core is about 7000 km in diameter with a temperature of 6000oC and a pressure of over 3 million atmospheres. The inner core is a lumpy solid iron sphere and the outer core is a thick liquid iron layer.
PHYSICAL STRUCTURE
lithosphere. Equivalent in part to the crust, the lithosphere comprises of a number of tectonic plates that 'float' on the asthenosphere.
asthenosphere. Ductile rocks that lie from below the lithosphere to 250 km below the surface.
mesosphere. Solid rocks below the asthenosphere.
COUNTRIES OF THE WORLD
COUNTRY | CAPITAL | CURRENCY | LANGUAGE | RELIGION | TIME ZONE |
| Afghanistan | Kabul | afghani | Pushto, Dari | Muslim | +4 |
| Albania | Tirana | lek | Albanian | Orthodox Christian | +1 |
| Algeria | Algiers | dinar | Arabic, French, Berber | Muslim | +1 |
| Andorra | Andorra La Vella | franc/peseta | Catalan, Spanish | RC | +1 |
| Angola | Luanda | kwanza | Portuguese | RC, Animist | +1 |
| Antigua & Barbuda | St Johns (On Antigua) | E.Caribbean dollar | English | Anglican | +4 |
| Argentina | Buenos Aires | austral | Spanish | RC | +3 |
| Armenia | Yerevan | dran | Armenian | Orthodox | +4 |
| Australia | Canberra | Australian dollar | English | Anglican, RC | +8 to +10 |
| Austria | Vienna | Euro | German | RC | +1 |
| Azerbaijan | Baku | manat | Azeri | Muslim | +1 |
| Bahamas | Nassau | Bahamian dollar | English, Creole | Baptist, RC | +5 |
| Bahrain | Manama | dinar | Arabic | Muslim | +3 |
| Bangladesh | Dhaka | taka | Bangala (Bengali) | Muslim | +6 |
| Barbados | Bridgetown | Barbados dollar | English | Anglican | +4 |
| Belarus | Minsk | rouble | Russian | Russian Orthodox | +2 |
| Belgium | Brussels | Euro | Flemish, French | RC | +1 |
| Belize | Belmopan | Belize dollar | English, Creole, Spanish | RC | +6 |
| Benin | Porto Novo | franc | French, Fon | Animist, Islam | +1 |
| Bhutan | Thimphu | ngultrum | Dzongkha (Tibetan), Nepali | Buddhist, Hindu | +6 |
| Bolivia | La Paz | boliviano | Spanish, Aymara, Quechua | RC | +4 |
| Bosnia-Herzegovina | Sarajevo | dinar | Serbo-croat Islam, Serbian | Orthodox | +1 |
| Botswana | Gaborone | pula | English, Setswana | Christian, Animist | +2 |
| Brazil | Brasilia | cruzeiro | Portuguese | RC | +3 to +4 |
| Brunei | Bandar Seri Begawan | Brunei dollar | Malay, Chinese | Muslim, Buddhist | +8 |
| Bulgaria | Sofia | lev | Bulgarian, Turkish | Orthodox | +2 |
| Burkina Faso | Ouagadougou | franc | French | Animist, Muslim | +0 |
| Burundi | Bujumbura | franc | Kirundi, French | RC, Animist | +2 |
| Cambodia | Phnom Penh | new riel | Khmer, French | Buddhist | +7 |
| Cameroon | Yaounde | franc | French, English | RC, Animist, Muslim | +1 |
| Canada | Ottawa | Canadian dollar | French, English | RC, Protestant | +5 to +8 |
| Cape Verde Islands | Praia Verdean | escudo | Portuguese, Creole | RC | +1 |
| Central African Republic | Bangui | franc | French, Sangho | Protestant, RC | +1 |
| Chad | N'djamena | franc | French, Arabic | Muslim, Animist | +1 |
| Chile | Santiago | peso | Spanish | RC | +4 |
| China (Inc.tibet) | Peking | yuan | Mandarin (Chinese) | Taoism, Buddhism and Confucianism | +8 |
| Colombia | Bogota | peso | Spanish, Indigenous Languages | RC | +? |
| Comoros | Moroni | franc | French, Arabic | Muslim | 3 |
| Congo | Brazzaville | franc | French, Lingala, Monokutuba,, Kongo | Animist, Christian | +1 |
| Costa Rica | San Jose | Spanish | RC | +6 | |
| Cote d'Ivoire | Yamoussoukro | franc | French | Animist, RC | 0 |
| Croatia | Zagreb | kuna | Croat, Serbian | RC | +1 |
| Cuba | Havana | peso | Spanish | RC | +5 |
| Cyprus | Nicosia | pound | Greek/Turkish | Greek Orthodox, Muslim | +2 |
| Czech Republic | Prague | koruna | Czech | RC | +1 |
| Democratic Rep of Congo | Kinshasa | zaire | French, Local Dialects | RC, Protestant | +1 |
| Denmark | Copenhagen | kroner | Danish | Lutheran | +1 |
| Djibouti | Djibouti | franc | French, Arabic | Muslim | +3 |
| Dominica | Roseau | E.Caribbean dollar | English | RC | +4 |
| Dominican Republic | Santo Domingo | peso | Spanish | RC | +4 |
| Ecuador | Quito | sucre | Spanish, Quechua | RC | +5 |
| Egypt | Cairo | pound | Arabic | Muslim | +2 |
| El Salvador | San Salvador | colon | Spanish, Nahuatl | RC | +6 |
| Equatorial Guinea | Malabo | franc | Spanish | RC | +1 |
| Eritrea | Asmara | birr | Tigrinya, TigreArabic | Muslim,, Christian | +3 |
| Estonia | Tallinn | kroone | Estonian, Russian | Lutheran | +2 |
| Ethiopia | Addis Ababa | birr | Amharic, Arabic | Oromo, Muslim, Orthodox Christian | +3 |
| Fiji | Suva | Fijian dollar | English, Fijian, Hindi | Methodist, Hindu | +12 |
| Finland | Helsinki | Euro | Finnish, Swedish | Lutheran, Orthodox Christian | +2 |
| France | Paris | Euro | French | RC | +1 |
| Gabon | Libreville | franc | French, Fang | RC | +1 |
| Gambia | Banjul | dalasi | English | Muslim, Protestant | 0 |
| Georgia | Tbilisi | rouble | Georgian | Orthodox | +4 |
| Germany | Berlin | Euro | German | Lutheran, RC | +1 |
| Ghana | Accra | new cedi | English | Animist, Christian, Muslim | 0 |
| Greece | Athens | Euro | Greek | Greek Orthodox | +2 |
| Grenada | St Georges | E.Caribbean dollar | English | RC, Anglican | +4 |
| Guatemala | Guatemala City | quetzal | Spanish, Mayan Dialects | RC, Protestant | +6 |
| Guinea-Bissau | Bissau | peso | Portuguese, Creole | Animist, Muslim | 0 |
| Guinea | Conakry | franc | French, Fulami | Muslim | 0 |
| Guyana | Georgetown | dollar | English, Hindi, Urdu | Hindu, Christian | +3 |
| Haiti | Port-au-Prince | gourde | French, Creole | RC, Voodoo | +5 |
| Honduras | Tegucigalpa | lempira | Spanish | RC | +6 |
| Hungary | Budapest | forint | Magyar | RC | +1 |
| Iceland | Reykjavik | krona | Icelandic | Evangelical Lutheran | 0 |
| India | New Delhi | rupee | Hindi, English & 1600 Languages | Hindu, Isalm | +5 |
| Indonesia | Jakarta | rupiah | Bahasa, Indonesian, Javanese | Muslim | +7 to +8 |
| Iran | Tehran | rial | Farsi, Azeri | Muslim | +3 |
| Iraq | Baghdad | dinar | Arabic, Kurdish | Muslim | +3 |
| Ireland | Dublin | Euro | Gaelic, English | RC | 0 |
| Israel | Jerusalem | shekel | Hebrew, Arabic | Judaism | +2 |
| Italy | Rome | Euro | Italian | RC | +1 |
| Jamaica | Kingston | Jamaican dollar | English, Creole | Protestant, Rastafarian | +5 |
| Japan | Tokyo | yen | Japanese | Shinto, Buddhism | +9 |
| Jordan | Amman | dinar | Arabic | Muslim | +2 |
| Kazakhstan | Alma-ata | tenge, rouble | Russian, Kazakh | Muslim, RC | +5 to 6 |
| Kenya | Nairobi | shilling | Swahili, English | Protestant, RC | +3 |
| Kiribati | Bairiki (On Tarawa) | Australian dollar | I-kiribati, English | RC, Protestant | +12 |
| Korea DPR | Pyongyang | won | Korean | Daoist, Confusianism | +9 |
| Korea, Republic of | Seoul | won | Korean | Buddhist, Protestant, Taoism | +9 |
| Kuwait | Kuwait City | dinar | Arabic | Muslim | +3 |
| Kyrgyzstan | Frunze | som, rouble | Kighiz | Muslim | +5 |
| Laos | Vientiane | kip | Lao | Buddhist | +7 |
| Latvia | Riga | lats | Lettish, Russian | Lutheran | +2 |
| Lebanon | Beirut | pound | Arabic | Muslim, Christian | +2 |
| Lesotho | Maseru | loti | Sesotho, English | RC, Protestant | +2 |
| Liberia | Monrovia | dollar | English | Animist, Muslim, Christian | 0 |
| Libya | Tripoli | dinar | Arabic | Muslim | +1 |
| Liechtenstein | Vaduz | franc | German | RC | +1 |
| Lithuania | Vilnius | litas | Lithuanan | RC | +2 |
| Luxembourg | Luxembourg | Euro | Letzeburgesch, French, German | RC | +1 |
| Macedonia | Bitolj | denar | Macedonia, Albanian | Orthodox | +1 |
| Madagascar | Antananarivo | franc | Malagasy, French | Animist, RC | +3 |
| Malawi | Lilongwe | kwacha | English, Chichewa | Christian | +2 |
| Malaysia | Kuala Kumpar | ringgit | Malay, English, Chinese | Muslim | +8 |
| The Maldives | Male | rufiyaa | Dhivehi | Muslim | +5 |
| Mali | Bamako | franc | French, Bambara | Muslim | 0 |
| Malta | Valletta | franc | Maltese, English | RC | +1 |
| Marshall Islands | Dalap-Uliga-Darrit | US dollar | Marshallese, English | Protestant | +12 |
| Mauritania | Nouakchott | ouguiya | Arabic, French | Muslim | 0 |
| Mauritius | Port Louis | rupee | English, Creole | Hindu, Christian, Islam | +4 |
| Mexico | Mexico City | peso | Spanish | RC | +6 |
| Micronesia | Palikir (On Pohnpei) | US dollar | English, Trukese, Ponapean | Protestant | +11 |
| Moldova | Kishinev | leu | Moldovan, Ukranian, Russian Russian | Orthodox | +2 |
| Monaco | Monaco-ville | franc | French | RC | +1 |
| Mongolia | Ulan-Baatar | tugrit | Kalkh, Mongolese | Buddhism | +8 |
| Morocco | Rabat | dirham | Arabic, Berber | Muslim | 0 |
| Mozambique | Maputo | metical | Portuguese | Animist, RC, Islam | +2 |
| Myanmar | Yangon | kyat | Burmese | Buddhist | +6 |
| Namibia | Windhoek | rand | Afrikaans, English | Lutheran, Various Christian | +2 |
| Nauru | Yaren District | Australian dollar | Nauruan | RC, Nauran Protestant Church | +12 |
| Nepal | Kathmandu | rupee | Nepali, Bilhari | Hindu | +5 |
| Netherlands | Amsterdam | Euro | Dutch | RC, Netherlands Reform Church | +1 |
| New Zealand | Wellington | New Zealand dollar | English, Maori | Anglican, RC | +12 |
| Nicaragua | Managua | cordoba | Spanish, Miskito | RC | +6 |
| Niger | Niamey | franc | French, Hausa | Muslim | +1 |
| Nigeria | Lagos | naira | English, Local Dialects | Muslim, Christian | +1 |
| Norway | Oslo | krone | Norwegian | Evangelical, Lutheran | +1 |
| Oman | Muscat | rial | Arabic | Muslim | +4 |
| Pakistan | Islamabad | rupee | Urdu, Punjabi, Sindhi, English | Muslim | +5 |
| Panama | Panama City | balboa | Spanish | RC | 5 |
| Papua New Guinea | Port Moresby | kina | English | Protestant, RC | +10 |
| Paraguay | Ascuncion | guarani | Spanish, Guran | RC | +4 |
| Peru | Lima | inti | Spanish, Quechua | RC | 5 |
| The Philippines | Manila On Luzon) | peso | Tagalog (Filipino) | RC | 8 |
| Poland | Warsaw | zloty | Polish | RC | +1 |
| Portugal | Lisbon | Euro | Portuguese | RC | +1 |
| Qatar | Doha | riyal | Arabic | Muslim | +3 |
| Romania | Bucharest | leu | Romanian | Romanian Orthodox, RC | +2 |
| Russia | Moscow | rouble | Great Russian | Russian Orthodox | +2 to 12 |
| Rwanda | Kigali | franc | French, Kinyarwanda | RC, Animist | +2 |
| St Christopher & Nevis | Basseterre | E.Caribbean dollar | English | Anglican, Methodist | 4 |
| St Lucia | Castries | E.Caribbean dollar | English, French Patois | RC | 4 |
| St Vincent & Grenedines | Kingstown | E.Caribbean dollar | English | Anglican, Methodist | 4 |
| San Marino | San Marino | lira | Italian | RC | +1 |
| Sao Tome & Principe | Sao Tome | dobra | Portuguese | RC | 0 |
| Saudi Arabia | Riyadh | riyal | Arabic | Muslim | +3 |
| Senegal | Dakar | franc | French, Wolof | Muslim | 0 |
| Seychelles | Victoria | rupee | Creole, English, French | RC | +4 |
| Sierra Leone | Freetown | leone | English, KrioMende,, Temne | Animist, Muslim | 0 |
| Singapore | Singapore City | dollar | Chinese, Malay, English | Buddhism, Daoism | +8 |
| Slovakia | Bratislava | koruna | Slovak, Hungarian RC | +1 | |
| Slovenia | Ljubljana | tolar | Slovene | RC | +1 |
| Solomon Islands | Honiara | Soloman Islands dollar | English, Pidgin English | Anglican, RC | +11 |
| Somalia | Mogadishu | shilling | Somali, Arabic | Muslim | +3 |
| South Africa | Pretoria/Cape Town | rand | Xhosa, Zulu, English, Afrikaans | Black African Churchs, Africaans Reform Church | +2 |
| Spain | Madrid | Euro | Spanish, Castilian | RC | +1 |
| Sri Lanka | Colombo | rupee | Sinhala, Tamil English | Buddhist, Hindu | +5 |
| Sudan | Khartoum | pound | Arabic | Muslim | +2 |
| Surinam | Paramaribo | guilder | Dutch, Sranang, Togo, Hindi | Hindu, RC, Muslim | +3 |
| Swaziland | Mbabane | lilangeni | Siswati, English | Various Christian & Indian | +2 |
| Sweden | Stockholm | krona | Swedish | Lutheran | +1 |
| Switzerland | Berne | franc | German | RC, Protestant | +1 |
| Syria | Damascus | pound | Arabic | Muslim | +2 |
| Tajikistan | Dushanbe | rouble | Tadzhik, Uzbek, Russian | RC, Islam | +3 |
| Tanzania | Dodoma | shilling | English, Swahili | Animist, Muslim, Christian | +3 |
| Thailand | Bangkok | baht | Thai, Chinese | Buddhist | +7 |
| Togo | Lome | franc | French, Ewe, Kabiye | Animist, RC | 0 |
| Tonga | Nuku'alofa | pa'anga | Tongan, English | Methodist | +13 |
| Trinidad & Tobago | Port of Spain | Trinidad & Tobago dollar | English, Hindi | RC, Protestant, Hindu | 4 |
| Tunisia | Tunis | dinar | Arabic | Muslim | +1 |
| Turkey | Ankara | lira | Turkish, Kurdish | Muslim | +2 |
| Turkmenistan | Ashkhabad | manat, rouble | Turkmen | Muslim | +5 |
| Tuvalu | Funafuti | Tuvalu dollar | Tuvaluan, English | Protestant Church of Tuvalu | +12 |
| Uganda | Kampala | shilling | English, Swahili | RC, Animist, Protestant | +3 |
| Ukraine | Kiev | karbvanets | Ukranian, Russian | Ukranian Orthodox | +2 |
| United Arab Emirates | Abu Dhabi | dirham | Arabic | Muslim | +4 |
| United Kingdom | London | pound | English | Anglican, RC | 0 |
| United States of America | Washington DC | US dollar | English | RC, Baptist | +5 to +8 |
| Uruguay | Montevideo | nuevo peso | Spanish | RC | +3 |
| Uzbekistan | Tashkent | som, rouble | Uzbek | Muslim | +5 to 6 |
| Vanuatu | Vila (On Efate) | vatu | Bislamay, English, French | Protestant, RC | +11 |
| Vatican City State | Euro | Italian, Latin | RC HQ | +1 | |
| Venezuela | Caracas | bolivar | Spanish | RC | 4 |
| Vietnam | Hanoi | dong | Vietnamese | Buddhist | +7 |
| Western Samoa | Apia (On Upolu) | tala | English, Samoan | Protestant, Congregational, RC | 11 |
| Yemen | Sana'a | rial | Arabic | Muslim | +3 |
| Yugoslavia | Belgrade | dinar | Serb | Orthodox, Islam | +1 |
| Zambia | Lusaka | kwacha | English, Tonga, Bemba | Animist | +2 |
| Zimbabwe | Harare | dollar | English | Animist, Anglican, RC | +2 |
WEATHER TERMS
anti-cyclone. An area of slowly rotating high atmospheric pressure. Cloud formation is restricted and the weather is usually settled.
atmospheric pressure. The weight of the air at a specific location and height.
depression. An rotating area of low atmospheric pressure. The rotation of the depression generates circulating winds.
dew. Water condensed at night from the bottom layer of air.
drizzle. Fine droplets of rain less than 0.5 mm in size.
drought. Long period of dry weather.
climate. The prevailing weather conditions in a particular area.
clouds. Water evaporating from the Earth's surface is held as a vapour in rising warm air. As the air cools the vapour condenses into water droplets which form clouds. Clouds are classified into two main groups: cumulus and stratus (massed and layered). Click here.
cyclone. A depression.
fog. A mass of cool air filled with tiny droplets forming upwards from ground level.
front. A thermal wall across which there is a rapid temperature change. The source of most bad or unsettled weather.
frost. Water that freezes a ground level when the air temperatures falls below 0oC.
hail. Ice particles about 5 mm in diameter formed about dust particles.
high. An anti-cyclone.
isobars. The lines on a weather map that indicate areas of equal air pressure. Tightly packed isobars indicate unsettled weather.
lightning. Discharge of an electric field from a cloud.
low. A depression.
mist. A mass of cool air filled with tiny droplets close to ground level.
precipitation. Water that reaches the ground.
rain. Falling water droplets greater than 0.5 mm in size.
seasons. Climatic changes caused by the position of the earth relative to the sun. The temperate zones have 4 seasons and the tropics two.
shower. A heavy, short lived period of precipitation.
sleet. A mixture of rain and snow.
snow. Ice crystals that 'grow' in clouds.
weather. The daily changes in the atmospheric conditions, primarily the movement of air. In the temperate zones the most influential phenomena are the changes in air pressure. These changes generate the clouds, windand rain that we call the weather.
wind. Wind is the lateral movement of air from high to low pressure areas.
WIND
anabatic. A wind that blows up mountain slopes.
breeze. Winds less than 50km/hr.
cyclone. Area of low pressure often giving rise to violent storms.
foehn wind. Dry, warm air blowing down a mountain.
gale. Winds between 51 and 87 km/hr.
hurricane. Winds in excess of 119 km/hr. A tropical cyclone in the Caribbean and North Atlantic.
jet stream. Strong continuous wind at high altitudes, usually blowing west to east.
katabatic. Gravity induced downward movement of air.
prevailing wind. The predominate wind in a particular area.
roaring forties. Strong westerly winds in the latitudes 40o to 50oS.
squall. Short lived wind in the opposite direction as the prevailing wind.
storm. Winds between 88 and 119km/hr.
tornado. A very strong whirlwind usually less than 500m in diameter, travelling between 20 and 60km/h.
trade winds. Regular winds blowing from sub-tropical to equatorial regions.
typhoon. Tropical cyclone (hurricane) particularly in the China Sea.
whirlwind. A narrow column of rapidly rotating air.
GLOSSARY OF MATHEMATICAL TERMS
Mathematics is the group of sciences concerned with the study of number, quantity, shape and space and their relationships with each other. The four main divisions of mathematics are arithmetic, algebra, geometry and calculus.
algebra. The substitution of symbols and letters for numerical variables and constants. These symbols can be manipulated in the same way as numbers and form the basis for most mathematical calculations.
abscissa. The x-coordinate of a point in a 2-dimensional coordinate system.
absolute value. The positive value for a real number, disregarding the sign. Written |x|. For example, |3|=3, |-4|=4, and |0|=0.
algebraic equation. An equation of the form f(x)=0 where f is a polynomial.
algebraic number. A number that is the root of an algebraic polynomial. For example, sqrt(2) is an algebraic number because it is a solution of the equation x2 = 2.
angles. The inclination of one line to another. Angles are measured in degrees or radians. One revolution of a circle = 360° = 2pi radians.
annulus. The region enclosed by two concentric circles.
arithmetic. The manipulation of numbers by addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and extraction of roots.
arithmetic mean. The arithmetic mean of n numbers is the sum of the numbers divided by n.
average. Typically this refers to the arithmetic mean.
base. The number of single digit numerals in a counting system. The decimal system has base 10 (0,1,2,...,9) and the binary system base 2 (0 and 1). In the expression xy, x is called the base and y is the exponent.
binary number. A number written to base 2.
binary operation. A binary operation is an operation that involves two operands. For example, addition and subtraction are binary operations.
binomial. An expression that is the sum of two terms such as a + b or a - b.
binomial coefficient. The coefficients of x in the expansion of (x+1)n.
bisect. To cut in half.
calculus. The study of continuous change in functions. The two branches of calculus are differentiation and integration. Differentiation is the determination of the rate of change in a function. Integration is the summation of the changes in a function, normally regarded as the area under a curve.
catenary. A curve whose equation is y = (a/2)(e x/a + e -x/a). A chain suspended from two points forms this curve.
central angle. An angle between two radii of a circle.
chord. The line joining two points on a curve is called a chord.
circle. The set of points equidistant from a given point (the center). A circle is the path proscribed by point that rotates about a fixed origin.

circular cone. A cone whose base is a circle.
circumcenter. The circumcenter of a triangle is the center of the circumscribed circle.
circumcircle. The circle circumscribed about a figure.
coefficient. The number part of an algebaric term: in 4x², 4 is the coefficient.
complementary angles. Two angles whose sum is 90o.
complex number. The sum of a real number and an imaginary number, for example 3+4i where i=sqrt(-1).
concave. Curved from the inside.
congruent figures. two geometric figures that are identical in size and shape.
conic section. The cross section of a right circular cone cut by a plane. An ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola are conic sections.
coordinate geometry. System of geometry where points, lines, shape and surfaces are represented by algebraic expressions. These expressions can be presented as graphical solutions (graphs) in two of three dimensions.
cubic equation. A polynomial equation of degree 3.
decimal number. A number written to the base 10.
deficient number. A positive integer that is larger than the sum of its proper divisors.
degree. The degree of a term in one variable is the exponent of that variable. For example, the degree of 7x5; is 2.
denominator. In the fraction x/y, x is called the numerator and y is called the denominator.
diagonal. In a polygon, the line segment joining a vertex with another (non-adjacent) vertex is called a diagonal.
diameter. The longest chord of a figure. In a circle, a diameter is a chord that passes through the center of the circle.
differential calculus. That part of calculus that deals with the opeation of differentiation of functions.
digit. In the decimal system, one of the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.
dihedral angle. The angle formed by two planes meeting in space.
dividend. In the expression "a divided by b", a is the divident and b is the divisor.
divisor. In the expression "a divided by b", a is the divident and b is the divisor.
dodecaedron . A solid having 12 plane faces.
domain. The domain of a function f(x) is the set of x values for which the function is defined.
duodecimal number system. The system of numeration with base 12.
elementary function. one of the functions: rational functions, trigonometric functions, exponential functions, and logarithmic functions.
ellipse . A closed plane curve generated by a point moving in such a way that the sums of its distances from two fixed points is a constant: a plane section of a right circular cone that is a closed curve. A plane figure whose equation is: x2/a2+y2/b2=1.
ellipsoid. A solid figure whose equation is x2/a2+y2/b2+z2/c2=1.
equation. A set of mathematical symbols split by an equals sign (=). Terms are symbols that are added or subtracted. Factors are symbols that are multiplied or divided.
equilateral polygon. A polygon all of whose sides are equal.
equilateral triangle. A triangle with three equal sides.
even number. An integer that is divisible by 2.
exponent. In the expression xy, x is called the base and y is called the exponent. See also index.
exponential function. The function f(x)=ex.
expoential function to base a. The function f(x)=ax.
factor. The integer divisors of a number. 1, 2 and 7 are the factors of 14.
factorial. n! (read n factorial) is equal to the product of the integers from 1 to n.
Fermat number. A number of the form 2(2n)+1.
Fibonacci number. A member of the sequence 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5,... where each number is the sum of the previous two numbers.
formula. A concise statement expressing the symbolic relationship between two or more quantities.
fraction. An expression of the form a/b.
frequency. The number of times a value occurs in some time interval.
frustum. For a given solid figure, a related figure formed by two parallel planes meeting the given solid. In particular, for a cone or pyramid, a frustum is determined by the plane of the base and a plane parallel to the base. NOTE: this word is frequently incorrectly misspelled as frustrum.
Gaussian curve. A normal curve.
geometry. The study of two and three dimensional space.
geometric progression. A sequence in which the ratio of each term to the preceding term is a given constant.
geometry. The branch of mathematics that deals with the nature of space and the size, shape, and other properties of figures as well as the transformations that preserve these properties.
golden ratio. (1+Sqrt[5])/2.
graph. A graph is a set of points (called vertices) and a set of lines (called edges) joinging these vertices.
great circle. A circle on the surface of a sphere whose center is the center of the sphere.
greatest common divisor/factor. The greatest common divisor of a sequence of integers, is the largest integer that divides each of them exactly.
hexagon . A plane figure having six sides and six angles.
hyperbola. A plane curve generated by a point so moving that the difference of the distances from two fixed points is a constant: a curve formed by the intersection of a double right circular cone with a plane that cuts both halves of the cone. A curve with equation x2/a2-y2/b2=1. or 2+y2/b2-z2/c2=-1.
hypotenuse. The longest side of a right triangle.
icosaedron . A polyhedron having 20 faces.
identities.. Algebraic relationships:
(a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2 (a + b)(a - b ) = (a2 - b2) a(b + c) = ab + ac 1/a - 1/b = (b -a)/(ab)
imaginary number. A complex number of the form xi where x is real and i=sqrt(-1).
imaginary part. The imaginary part of a complex number x+iy where x and y are real is y.
index. A superscript indicating the number of times a number is multiplied by itself. Examples of indexes are:
an x am = a(n +m) a-n = 1/an a1/n = nÖa (an)m = anm
inequality. The statement that one quantity is less than (or greater than) another.
infinitesimal. A variable that approaches 0 as a limit.
inflection. A point of inflection of a plane curve is a point where the curve has a stationary tangent, at which the tangent is changing from rotating in one direction to rotating in the oppostie direction.
integer. One of the numbers ..., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ... A whole number.
irrational number. Any real number that is not rational, that is it cannot be written as a terminating or repeating decimal. These include p, e and Ö2.
isosceles tetrahedron. A tetrahedron in which each pair of opposite sides have the same length.
isosceles triangle. A triangle with two equal sides.
isosceles trapezoid. Ain which the two non-parallel sides have the same length.
least common multiple. The least common multiple of a set of integers is the smallest integer that is an exact multiple of every number in the set.
linear function. A function of the form y=ax+b.
line segment. The part of a line between two given distinct points on that line (including the two points).
logarithm. A logarithm is the exponent of a number to a specified base. Ifbn = x then n is the logarithm of x to the base b.
lowest common denominator. The smallest number that is exactly divisible by each denominator of a set of fractions.
major axis. The major axis of an ellipse is it's longest chord.
maximum. The largest of a set of values.
mensuration. The act of measuring. Geometry applied to the computation of lengths, areas, or volumes from given dimensions or angles.
minor axis. The minor axis of an ellipse is its smallest chord.
minimum. The smallest of a set of values.
mode. The most frequently occurring value in a sequence of numbers.
multiple. The integer b is a multiple of the integer a if there is an integer d such that b=da.
natural number. Any one of the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ... .
negative number. A number smaller than 0.
normal. perpendicular
numbers. Numbers are either real or complex. Real numbers are those used for counting and range from - to + . Complex numbers are those that contain Ö-1 , usually denoted i so that i2 = -1.
number line. A line on which each point represents a real number.
numerator. In the fraction x/y, x is called the numerator and y is called the denominator.
oblique angle. an angle that is not 90o
oblique triangle. A triangle that is not a right triangle.
obtuse angle. an angle larger than 90o but smaller than 180o
obtuse triangle. A triangle that contains an obtuse angle.
octagon . A plane figure having eight angles and eight sides.
octoedron . A solid bounded by eight plane faces.
odd number. An integer that is not divisible by 2.
ordinate. The y-coordinate of a point in the plane.
origin. The point in a coordinate plane with coordinates (0,0).
parabola . A plane curve generated by a point moving so that its distance from a fixed point is equal to its distance from a fixed line: the intersection of a right circular cone with a plane parallel to an element of the cone.
parallel . Lying or extending alongside of one another and always at the same distance apart; continuously equidistant: said of two or more lines, surfaces, or concrete things.
parallelogram . A four-sided rectilineal figure whose opposite sides are parallel but the internal angles are greater or less than 90 degrees.
percentage. A number represented as a fraction of 100. Percentages may be written as a proper fraction or as a decimal fraction, ie: 48% is 48/100 or 0.48.
perfect number. A positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors. For example, 28 is perfect because 28=1+2+4+7+14.
perpendicular . Situated at right angles to the plane of the horizon, or directly up or down; vertical.
prime. A prime number is an integer larger than 1 whose only positive divisors are 1 and itself.
Pythagorean triangle. A right triangle whose sides are integers.
platonic solids (polyhedrons). Solids with faces of equal shape. There are only five:
Tetrahedron - 4 triangular faces Cube - 6 square faces Octahedrons - 8 triangular faces Dodecahedron - 12 pentagonal faces Icosahedron - 20 triangular faces
Tetrahedron - 4 triangular faces Cube - 6 square faces Octahedrons - 8 triangular faces Dodecahedron - 12 pentagonal faces Icosahedron - 20 triangular faces
polygons. Figures with sides of equal length and equal internal angles. The first 10 are:
Triangle - 3 sides Quadrangle - 4 sides Pentagon - 5 sides Hexagon - 6 sides Heptagon - 7 sides Octagon - 8 sides Nonagon - 9 sides Decagon -10 sides Dodecagon - 12 sides Icosagon - 20 sides
Triangle - 3 sides Quadrangle - 4 sides Pentagon - 5 sides Hexagon - 6 sides Heptagon - 7 sides Octagon - 8 sides Nonagon - 9 sides Decagon -10 sides Dodecagon - 12 sides Icosagon - 20 sides
power. A general term for squares, cubes etcetera. See index.
primes. Numbers whose only factors are 1 and itself. Unity (1) is not a prime. The first seven primes are: 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17 and 19.
probability. The likelyhood that something will happen.
Pythagoras' Theorem. For any right-angled triangle, the square of the longest side (R) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (xand y)
QED. Abbreviation for quod erat demonstrandum, used to denote the end of a proof.
quadrangular prism. A prism whose base is a quadrilateral.
quadrangular pyramid. A pyramid whose base is a quadrilateral.
quadrant. Any one of the four portions of the plane into which the plane is divided by the coordinate axes.
quadratic equation. An equation of the form f(x)=0 where f(x) is a second degree polynomial. That is, ax2 + bx + c = 0.
quadrilateral. A geometric figure with four sides.
quotient. The result of a division.
radians. Circular measure where the circumference of a circle is divided in to a number of arcs each equal in length to the radius. There are 2pi radians in 1 revolution. One radian = 180/pi degrees. One radian is approximately 57.3o.
ratio. quotient of two numbers.
rational number. A rational number is a number that is the ratio of two integers. All other real numbers are said to be irrational. All rational numbers can be written as a terminating or repeating decimal.
real part. The real number x is called ther eal part of the complex number x+iy where x and y are real and i=sqrt(-1).
reciprocal. A number divided into 1. The reciprocal of 7 is 1/7.
reflex angle. An angle between 180o and 360o.
rhombus. A parallelogram with four equal sides.
right angle. an angle formed by two perpendicular lines; a 90o angle.
right triangle. A triangle that contains a right angle.
scalene triangle. A triangle with unequal sides.
secant. A straight line that meets a curve in two or more points.
sequence. A collection of numbers in a prescribed order: a1, a2, a3, a4, ...
series. The sum of a finite or infinite sequence
similar figures. Two geometric figures are similar if their sides are in proportion and all their angles are the same.
spherical trigonometry. The branch of mathematics dealing with measurements on the sphere.
square. A quadrilateral with 4 equal sides and 4 right angles.
square number. A number of the form n^2.
supplementary. Two angels are supplementary of they add up to 180o.
tangent. A line that meets a smooth curve at a single point and does not cut across the curve.
torus. A geometric solid in the shape of a donut.
transcendental number. A number that is not algebraic.
trapezium. A quadrilateral in which no sides are parallel.
trapezoid. A quadrilateral in which two sides are parallel.
triangle. A geometric figure with three sides. The sum of the internal angles of any triangle is 180 . The four basic triangle types are:
right-angled - one angle equal to 90o isosceles - two sides of equal length equilateral -all sides of equal length scalene -no equality in any of the sides.
right-angled - one angle equal to 90o isosceles - two sides of equal length equilateral -all sides of equal length scalene -no equality in any of the sides.
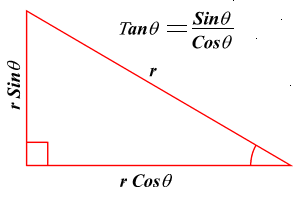
trigonometry. The branch of mathematics exploiting the properties of right angled triangles. The trigonometric identities are: sine, cosine and tangent and are determined as follows:
truncated pyramid. A section of a pyramid between its base and a plane parallel to the base.
twin primes. Two prime numbers that differ by 2. For example, 11 and 13 are twin primes.
unilateral surface. A surface with only one side, such as a Moebius strip.
unit circle. A unit circle is a circle with radius 1.
unit cube. A cube with edge length 1.
unit fraction. A fraction whose numerator is 1.
unit square. A unit square is a square of side length 1.
unity. one
volume. The measure of spce occupied by a solid body.
vulgar fraction. A common fraction.
whole number. A natural number.
x-axis. The horizontal axis in the plane.
x-intercept. The point at which a line crosses the x-axis.
y-axis. The vertical axis in the plane.
y-intercept. The point at which a line crosses the y-axis.
HUMAN ANATOMY
The human body can be broken down into a number of systems for example: brain and nervous system, circulatory system, reproductive system, the skin and skeleton. Listed below are the major organs in each system.
- adam's apple. The popular name for the thyroid cartilage The lump seen on the front of the throat of men. It is small and invisible in females.
- abdomen. The lower part of the torso containing the Stomach, intestine, kidneys, liver and reproductive organs.
- adrenal gland. Endocrine gland above kidneys producing adrenaline (a heart stimulant) and other hormones.
- adipose tissue. A form of connective tissue in which the constituent cells are modified to enable them to contain droplets of oil. (Fat).
- alimentary canal. The food processing tube running from mouth to anus, about 9m long.
- alveolus. Sac in lungs absorbing oxygen from the air into the blood.
- anus. Excretory opening at end of alimentary canal.
- aorta. The largest artery in the human body. It carries blood from the heart to the arms, legs and head.
- artery. Blood vessel taking oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
- bile. secretion of the liver stored in the gall bladder.
- bladder. A sack in the abdomen which collects urine from the kidneys.
- blood. The main circulatory fluid: red and white blood cells transported in plasma.
- bowel. The division of the alimentary canal below the stomach, that is the intestines.
- bones. A matrix of collagen fibres providing support for other tissues. The hollow centre is filled with marrow, the source of blood cells.
- brain & nervous system. The nervous system is co-ordinated by the brain. All 13 000 million nerves originate in the brain, form the spinal column and branch off to the organs and tissues they control.
- bronchi. The bronchial tubes (bronchi) are a division of the trachea which branch repeatedly into small bronchioles within the lungs.
- caecum. First part of the large intestine.
- capillary. Very small blood vessel linking arteries and veins.
- cartilage. Soft, protective pad between the joints. Cartilage or cartilaginous tissue covers the ends of the bones where they come together to make a joint. It enables the bones to move easily.
- cardiac muscles. The heart muscles.
- cerebellum. Part of the brain at the back of the head that controls the muscles and postural equilibrium.
- cerebrum. Each of the two halves of the upper brain that occupies the whole of the dome of the cranium.
- colon. Central and major part of the large intestine.
- coronary artery. Artery providing blood for the heart.
- dermis. Living skin tissue containing capillaries, lymph vessels, nerve endings, pores and hair follicles.
- diaphragm. A large transverse muscle at the base of the thorax, used in respiration to draw air into the lungs.
- duodenum. First part of the small intestine.
- endocrine gland. A gland that secretes hormones into the body.
- epidermis. Layers of continually shedded skin cells.
- epithelium. A basic type of tissue. It comprises the external surface of the skin, the internal surfaces of the digestive, respiratory and urogenital systems and others.
- fallopian tubes. Two tubes that carry eggs from the ovary to the uterus. Eggs are fertilised in the Fallopian tubes by sperm, and then moved to the uterus.
- follicle. A small group of cells that surrounds and nourishes a structure such as a hair or a cell such as an egg.
- fontanelle. A membrane covered vault in the skull. It normally closes during infancy.
- gall bladder. A small muscular sac attached to the liver.
- ganglion. An enlargment somewhere in the course of a nerve, and containing nerve cells in addition to nerve filaments.
- gastric juice. Clear, colourless fluid secreted by the mucous membrane of the stomach, and is the chief agent in digestion.
- glands. Organs which produce substances (such as blood) for use within the body. Endocrine glands produce secretions at a distance from the tissues which they affect. Exocrine glands carry secretions through ducts to the site where they are required.
- haemoglobin. The protein that carries oxygen in the blood.
- heart. Muscular organ in chest that pumps blood to the lungs, tissues and other organs.
- hormone. A product of the endocrine glands.
- hypothalamus. Part of the brain that controls which regulates rhythmic activity, physiological stability, body temperature and the pituitary gland.
- ileum. Last part of the small intestine.
- intestine. The digestive tract. The small intestine (duodenum, jejunum and ileum) and large intestine (caecum, colon and rectum). The intestine breaks up digested food into those molecules required by the body.
- involuntary muscles. Those muscles we cannot control.
- jejenum. Central part of the small intestine.
- joint. A structure where two bones meet.
- jugular vein. Vein returning blood from the head to the heart.
- kidney. Organ which filters waste material from the blood.
- lachrymal gland. Exocrine gland beneath the upper eye lid which secretes tears
- larynx. A cavity at the top of the trachea containing the vocal cords.
- leucocyte. Colourless corpuscles; white blood cells.
- ligament. Fibrous band supporting bones and joints.
- liver. Large gland in the abdomen controlling many chemical processes. A nutrient storehouse.
- lungs. Organs in the thorax through which oxygen is absorbed into the blood and carbon dioxide expelled. The lungs draw about half a litre of air 14-16 times a minute.
- lymphatic system. System of tubes and glands that collect and filter waste fluid from the cells before returning it to the blood system.
- medulla oblongata. Lower part of the brain controlling the heart and lungs.
- muscles. Fibrous organs used to support the skeleton, provide movement or power the body's life support systems.
- nerve. Cord like structure built from a number of neurones along which nerve impulses are conveyed to different parts of the body.
- neurone. Nerve cell, many centimetres long with a microscopic diameter.
- oesophagus. The gullet, a muscular tube propelling food from trachea to stomach.
- organ. General name for any part of the body that has a specific purpose.
- ovary. One of two female reproductive organs. The ovaries house ova, unfertilized female gametes.
- pancreas. Large endocrine gland in the abdomen producing insulin and digestive juices.
- parathyroid glands. Two small glands in the neck concerned with the use of calcium in the body.
- parotid gland. Salivary gland.
- penis. Male reproductive organ.
- placenta. Organ connecting a foetus to the uterine wall. It is the organ by means of which the nutritive, respiratory and excretory functions of the foetus are carried on.
- pineal gland. Gland at the base of the brain controlling melatonin levels.
- pituitary gland. Master endocrine gland at the base of the brain controlling the other endocrine glands.
- plasma. Clear fluid in the circulatory system that transports blood cells.
- rectum. Last part of the the large intestine where waste material is stored prior to excretion.
- reproductive organs. Those organs used in the production of genetic material (testes and ovaries) or are involved in the reproductive process (penis, vagina, womb).
- saliva. A secretion from the salivary glands in the oral cavity. It contains mucus to lubricate food and enzymes.
- sclerous tissue. The stiffening which is essential for the formation of the general framework of the body. There are two types: cartilage and bone.
- sebaceous glands. Ducts in the skin which secrete oil to lubricate the skin and hair.
- skeleton. System of bones providing support for the body. Many of the bones are hinged (jointed) allowing the skeleton to move.
- skeletal muscles. Those muscles that we can control.
- skin. Dermoid Tissue, is composed of two layers, the cuticle, epidermis or epithelium and the corium or dermis.
- spleen. Organ that regulates the number of red blood cells.
- spleen. Organ in abdomen producing white and destroying red blood cells.
- subcutaneous layer. Layer of fatty tissue below the dermis.
- stomach. First part of the digestive tract where food is broken down by powerful acids into smaller components.
- tendon. Fibrous band joining muscle to bone.
- testes. Male reproductive organs that produce spermatozoa, unfertilized male gametes.
- thalamus. Small part of brain, used in mechanism of sensation.
- thorax. The chest cavity or upper bart of the torso containing the heart, lungs and oesophagus.
- tonsils. A pair of small organs on either side of the root of the tongue that protect the throat from infection.
- trachea. Wind pipe.
- thymus gland. Gland in the chest that disappears in adulthood. It is involved with immunity.
- thyroid gland. Endocrine gland in neck producing thyroxin regulating the metabolism.
- urethra. A canal which that channels urine from the bladder out of the body.
- vagina. Female reproductive organ.
- vein. Blood vessel returning deoxygenated blood to the heart.
- ventricle. Chambers within the heart which force blood along the arteries.
- womb. Female reproductive organ where the foetus gestates (develops). The uterus.
An adult human is made up from about 45 litres of water, 13 kg of carbon, enough phosphorous for 2200 matches, a spoonful of sulphur and enough iron for a 25 mm nail.
There are 10 000 million nerves controlled by the brain. An adult heart beats between 60-80 times a minute pumping 5.5 litres of blood around 10 000 km of blood vessels. The lungs draw about half a litre of air 14-16 times a minute. There are about 650 muscles in a human body. 250ml of fluid is lost every day through the feet. The alimentary tract is about 9m long. An adult skeleton contains 206 bones: 22 in the skull with 27 in each hand, 26 in each foot, 24 ribs, 32 teeth, 27 vertebrae and about 100 joints.
The amount of energy an adult requires just to stay alive will power a 75 watt light bulb.
ASTRONOMY - THE SOLAR SYSTEM
The solar system is about 4.6 million years old. It began as a spinning disc of hydrogen and helium which, over a period of 25 million years, formed into the sun and surrounding planets.

THE SUN
The Sun is a nuclear reactor generating energy by the conversion of hydrogen into helium. The rate of conversion is relatively slow, there is enough hydrogen for another 15 billion years.
The granular surface (photosphere) is constantly changing, the main features of which are sunspots and erupting jets of gas (spicules). Above the surface is a hydrogen chromosphere and beyond this is the corona. The Sun is classified as a G2 yellow dwarf.
THE TERRESTRIAL PLANETS
The inner four planets all have an iron core, rock mantle and a crust of varying thickness.
MERCURY
 |
Mercury, the innermost planet, is heavily cratered, very hot and has virtually no atmosphere. It spins very slowly, only three times in every two orbits of the sun.
Mean Orbit: 57 909 100 km Mean Diameter: 4 878 km Orbital Period1: 88.0 days Mass: 0.055 Satellites: None |
VENUS
 |
Venus is often the brightest object in the night sky due to the reflective cloud layer, the result of a hot carbon-dioxide atmosphere. The rocky surface is relatively flat with two pronounced highland regions, a temperature of over 800 C and prone to violent volcanic activity.
Mean Orbit: 108 208 600 km Mean Diameter: 12 102 km Orbital Period1: 224.7 days Mass: 0.815 Satellites: None |
EARTH
 |
The third planet, Earth, is so far the only one known to support life. Two thirds of the surface is covered by water and the atmosphere is mostly nitrogen-oxygen. See previous chapters for more information.
Mean Orbit: 149 598 600 km Mean Diameter: 12 756 km Orbital Period1: 365.3 days Mass: 1.000 Satellites: Moon |
MARS
 |
Mars: the red planet. The surface is barren and cratered with massive volcanos, deep chasms and two small polar ice caps. The red colour comes from the iron rich sand that is literally rusty. Mars has a thin carbon-dioxide atmosphere.
Mean Orbit: 227 939 200 km Mean Diameter: 6 794 km Orbital Period1: 687.0 days Mass: 0.107 Satellites: Phobos, Deimos. |
THE GAS GIANTS
So called because of their gaseous surfaces (albeit frozen), all the gas giants have ring systems of dust and ice fragments. In some cases the rings are 'shepherded' by small satellites.
JUPITER
 |
The largest planet in the solar system. Jupiter has a rocky core and a hydrogen/helium atmosphere the inner layers of which are very dense. The atmosphere is distorted by the high rotational speed causing the equator to budge. The circulating winds form coloured belts that include a huge storm called the Great Red Spot. The outermost satellites are probably captured asteroids.
Mean Orbit: 778 298 400 km Mean Diameter: 142 984 km Orbital Period11: 11.9 years Mass2: 317.828 Satellites: Metis, Adastra, Almathea, Thebe, Io, Europa, Ganymede, Callisto, Leda, Himalia, Lysithea, Elara, Ananke, Carme, Pasiphae, Sinope. |
SATURN
 |
Very similar to Jupiter in composition. Saturn has a distinctive ring system split into 7 main bands each containing hundreds of separate rings.
Mean Orbit: 1 426 394 000 km Mean Diameter: 120 536 km Orbital Period1: 29.5 years Mass2: 95.161 Satellites: Pan, Atlas, Prometheus, Pandora, Epimetheus, Janus, Mimas, Enceladus, Tethys, Telesto, Calypso, Dione, Helene, Rhea, Titan, Hyperion, Iapetus, Phoebe. |
URANUS
 |
Uranus, the seventh planet, has a rocky core, a frozen shell of water, methane and ammonia, and an atmosphere of hydrogen, helium and methane. Uranus has nine rings and the axis is horizontal: it rolls rather than spins round the sun.
Mean Orbit: 2 875 039 000 km Mean Diameter: 51 118 km Orbital Period1: 84.0 years Mass2: 14.536 Satellites: Cordelia, Ophelia, Bianca, Cressida, Desdemona, Juliet, Portia, Rosalind, Belinda, Puck, Miranda, Ariel, Umbriel, Titania, Oberon. |
NEPTUNE
 |
The structure of Neptune is similar to that of Uranus. The atmosphere contains distinctive, blue, fast moving clouds and the Great Dark Spot; a storm the size of Earth about which a smaller storm, the Scooter, orbits.
Mean Orbit: 4 504 450 000 km Mean Diameter: 49 600 km Orbital Period1: 164.8 years Mass2: 17.132 Satellites: Naiad, Thalassa, Despina, Galatea, Larissa, Proteus, Triton, Nereid. |
PLUTO
 |
Pluto is a small rocky planet with a thick ice mantle that orbits high out of the elliptic and, until 1999, was inside the orbit of Neptune.
Mean Orbit: 5 913 490 000 km Mean Diameter: 2 894 km Orbital Period1: 248.5 years Mass2: 0.002 Satellites: Charon. |
1. The orbital (sidereal) period is measured in "Earth" units. For example: 1 Mercury year = 88 Earth days.
2. The masses of the planets are given relative to the mass of the Earth which is 6 × 1021 tonnes.
2. The masses of the planets are given relative to the mass of the Earth which is 6 × 1021 tonnes.
POLITICS AND LAW - POLITICAL IDEOLOGIES
Ideologies are the sets of basic beliefs about the political, economic, social and cultural affairs held by the majority of people within as society.
absolutism. System where the rulers have unlimited control.
anarchism. Society without government, laws, police or other authority. System of self-control.
aristocracy. The privilege of social class whose members possess disproportionately large percentage of society's wealth, prestige and political influence.
autocracy. Supreme political power is in the hands of one person whose decision are unregulated..
capitalism. Right-wing political system where the principle means of production and distribution are in private hands.
communism. Extreme left-wing ideology based on the revolutionary socialist teachings of Marx. Collective ownership and a planned economy. Each should work to their capability and receive according to their needs.
conservatism. Governmental system where the existing institution are maintained, emphasizing free-enterprise and minimal governmental intervention.
democracy. Government by the people usually through elected representatives.
dictatorship. Government by a single person with absolute control over the resources of the state.
egalitaranism. Belief where all citizens have equal rights and privileges.
fascism. Extreme right-wing ideology where the existing social order is protected by the forcible suppression of the working class.
imperialism. The extension of power and rule beyond established geographical boundaries.
liberalism. Representative government, free-speech, abolition of class privilege and state protection of the individual.
Marxism. Developed by Marx and Engles, it proposes that all is subject to change and resistance to change necessitates the overthrow of the system through class struggle.
Maoism. Interpretation of Marxist communism emphasizing the development of agriculture.
Monarchy. A form of rule in which the head of state is a King or Queen.
nationalism. The unification of the state and release from foreign rule.
oligarchy. A system of government in which virtually all power is held a small number of wealthy people who shape policy to benefit themselves.
populism. Collective noun for the ideologies which demand the redistribution of political power and economic leadership to the 'common people'.
socialism. Left-wing political system where the principle means of production, distribution and exchange are in common ownership.
theocracy. Rule by the church.
totalitarianism. Government control of all activities.
Trotskyism. Form of Marxism incorporating the concept of permanent revolution.
THE LEFT
liberty. The freedom of speech and the right to dissent.
equality. A classless society with the redistribution of wealth through a welfare state.
fraternity. The communal brotherhood, working and living as one.
THE RIGHT
authority. The preservation of order through an evolved authority.
hierarchy. The continuation of the existing social order.
property. The right to private ownership.
CHRONOLOGY
1- PRE HISTORY (BC)
The term Pre-History means in general those events that took place before historical records were kept. As such many dates are approximate and others are traditional.
The migration of man from Central Africa had covered the globe by the end of the ice age. Neolithic communities became well established in Central and South America, China and across Asia but it was the fertile lands of Mesopotamia that saw the first organised civilisations. Most of Europe until the Roman invasions, consisted of Celtic communities.
8500 Rising sea level cuts Britain off from Europe.
5500 Wheel introduced into Europe.
5000 Agriculture spreads across Europe, start of megalith culture and copper working.
4000 Sumerians (the founders of Babylonian culture) settle in Mesopotamia, the land between the Euphrates and Tigris.
3200 Menes unites lower and upper Egypt.
3000 Start of Cornish tin mining.
2600 Pyramids of Gizeh built.
2200-1500 Height of Minoan civilisation on Crete.
2100-1600 Building and re-building of Stonehenge.
2006 Elamites capture City of Ur ending Sumerian civilisation.
1950 Babylonian Empire born from the meeting of two great avenues of commerce in Mesopotamia.
1800 Bronze working introduced into Britain.
1580 Hyksos invaders driven out of Egypt. New Kingdom founded, greatest period of Egypt's history.
1500-1130 Myceneans flourish in Southern Greece.
1230 Moses leads Israelites out of Egypt.
1180 Siege of Troy by Agamemnon leader of Greek forces.
1166 Rameses III, last great pharaoh of Egypt, dies.
1000 Iron age begins in Europe.
950 Foundation of Assyrian empire in Mesopotamia.
814 Phoenician emigrants from Tyre found Cartage on Gulf of Tunis.
776 First Olympiad.
2- ROMAN ERA
753 Rome founded.
750 Phoenician capital, Tyre, captured by Babylonians. Jimmu, first Mikado (Emperor) of Japan.
750-550 Greeks found trading colonies around Mediterranean and Black Sea.
612 Collapse of Assyrian Empire and founding of New Babylonia.
586 Jerusalem captured by Babylonians.
563 Birth of Buddha.
551 Confucius born in China.
550 Foundation of Persian Empire. At its height by 500BC: Asia Minor, Syria, Egypt, Iran and N India.
518 Etruscan dynasty in Rome expelled and republic established.
490 Invasion of Greece by Darius I of Persia defeated by Athenians at Marathon.
480 Thermopylae defended to the death by Spartan against Xerxes of Persia.
431-404 Peloponnesian War between Athens and Sparta.
390 Gauls capture and hold Rome to ransom.
336 Alexander (the Great) proclaimed King of Macedonia. By 332 had conquered most of Greece and Persian Empire.
323 Alexander dies, empire divided between his generals.
300 Invasion of Ireland by Gaels. Ireland divided into kingdoms subject to a high king elected under tribal (Brehon) law.
272 Rome completes conquest of Italy.
246 -221 Great Wall of China built.
241-146 Three Punic Wars between Rome and Cartage.
225 Gauls invade Roman territory but are defeated. For protection Rome extends borders northwards.
221 First Emperor of China.
166 Tartar invasion of China.
146 Greece annexed by Rome and Cartage destroyed.
102 German invasion of Italy repelled by Marius.
91-88 Italian cities revolt against the Roman Empire.
90 First British coinage introduced.
87 Greece attempts invasion of Rome.
73 Slaves revolt led by Spartacus is crushed by Crassus.
60 Alliance formed between Pompey, Crassus and Caesar.
55 (26 Aug) Julius Caesar makes exploratory expedition to Britain.
54 (18 or 21 July) Second Roman invasion, 5 legions and 2000 cavalry
51 Caesar conquers Gaul as far as the Rhine.
49 Civil War, Caesar emerges as the master of Rome.
45 Roman colonists settle in Cartage.
44 Caesar assassinated.
32 Rome's dominions are divided, Octavia in the west and Antony the east.
31 Octavia defeats Antony and Cleopatra at Actium.
30 Cleopatra dies. Egypt falls to Rome.
27 Octavia (as Augustus) becomes first true emperor of Rome.
4BC Birth of Jesus.
30AD Jesus crucified.
43 Third Roman invasion of England by Claudius and start of Roman occupation. English chieftain, Charactarus, resists.
61 Revolt by Bodicca (Boadicea). Colchester, London and St Albans sacked.
70 Titus captures Jerusalem and drives Jews from Holy Land.
78 Roman occupation of Wales.
79 Pompeii destroyed by eruption of Vesuvius. Colosseum completed.
80 Romans reach Scottish lowlands.
83 Subjugation of Britain by Romans.
117 Conquest of Macedonia marks the peak of Roman expansion.
127 Hadrian's Wall built by Aulus Platonius Nepos.
164 -180 Plagues ravage Roman and Chinese empires.
180-284 Continual invasion of Roman Empire by Franks, Goths, Parthians, Vandals and Huns.
284 -305 Roman Empire reorganised as a central autocracy.
330 Emperor Constantine moves capital to Byzantium (Constantinople).
364 Roman Empire splits, now ruled by Byzantium in the east and Rome in the west.
4- ANGLO SAXON
The fall of the Roman Empire in 476 was followed by the rise of the Byzantium and Arab empires. Britain until the 11th century was subjected to a series of invasions from mainland Europe.
417 -427 Partial Roman re-occupation of Britain.
432 Saint Patrick introduces Christianity to Ireland.
434 Attila, King of the Huns (Mongolians), invades Europe.
450 Start of Anglo-Saxon invasion of Britain (Angles, Franks, Friesians, Jutes and Saxons). Kingdoms of Wessex, Mercia and Northumbria established by 8th century.
455 Vandals attack Rome. Empire has 10 emperors in next twenty years.
476 The last Emperor of Rome is deposed and empire ceases to exist even in name.
482 Clovis crowns himself first King of France.
503 Battle of Mount Badon. Saxon advance halted by Britons, probably led by Arthur.
571 Birth of Mohammed.
597 Christianity introduced into Britain by St Augustine.
603 Scottish invasion of England halted in Northumbria.
616 Mohammed declares himself prophet of Allah.
632 Mohammed dies.
636 Arabs, led by Abu Bakr begin Islamic jihad. By 850 Arab Empire at its greatest extent: Spain, North Africa and Arabia and Indus Valley.
762 Foundation of Baghdad, Capital of Arab Empire.
787 Start of Viking raids on England and, over next two centuries, much of north Europe.
800 Charlemagne founds Holy Roman Empire.
829 Egbert of Wessex accepted as overlord of England.
844 Kenneth MacAlpine unites Picts and Scots into Kingdom of Scotland.
878 Alfred expels Danes from Wessex but cedes North and East of England.
900 England reconquered, national unity achieved.
910 Abbey of Cluny founded from which monastic reforms spread.
911 Normans granted control of Lower Seine Valley.
919 Separation of Frankish empire into France and Germany.
954 England unified under Athelstan.
962 Frankish Empire replaces Carolingian as head of Holy Roman Empire.
991 Danes resume raiding England.
1000 Lief Erickson reaches America.
1014 Vikings defeated in Ireland by Brian Boru at Clontarf.
1015 Malcolm II conquers South East of Scotland.
1016 -1042 England ruled by Danish Kings until expulsion by Edward the Confessor.
5- EARLY MIDDLE AGES
1066 Norman influence in England leads to Norman invasion and Battle of Hastings on 14th October. English rebellion ends with defeat of Hereward the Wake in 1071.
1086 Compilation of the Doomsday Book.
1095 Pope Urban II summons all Christian nations to the First Crusade against the Turks. The crusades continue until 1252.
1119 Order of the Knights Templar founded.
1167 Oxford University founded.
1170 Thomas Becket murdered in Canterbury Cathedral.
1171 Henry II invades and subjugates Ireland.
1174 Caliph Saladin begins Moslem holy war against Christianity.
1192 Richard I (Lionheart) held captive in Germany on 3rd Crusade. Brother John attempts to seize throne.
1194 -1282 Llewellyn I and II resist advance of Norman marcher barons into Wales.
1211-1215 Mongols under Genghis Khan invade China.
1215 Barons force King John to sign Magna Carta after his attempts to claim more than his entitlement of land. Pope vetoes Magna Carta starting 1st Barons' War.
1216 Peoples struggle against Henry III produces House of Commons.
1260 Mongol Empire at its greatest extent: Black Sea to Manchuria and much of southern Russia.
1264 -1267 2nd Barons' War.
1266 Hebrides ceded to Scotland by Norway.
1279 Farthing issued. Mongol leader, Kublai Khan becomes Emperor of China.
1282 Conquest of Wales by Edward I.
1291 Last Christian stronghold in Syria, Arce, falls to the Arabs.
1295 Formation of Edward I's Model Parliament; King, Lords and Commons.
1300 Foundation of Moslem Ottoman Empire in Turkey.
1314 Battle of Bannockburn, Robert Bruce defeats Edward II.
1315 -1317 Famine in Europe.
1328 Scottish independence recognised.
6- LATE MIDDLE AGES
England's claim to French crown leads to 100 Years War (1337 -1453) against alliance of France and Scotland. Defeat leads to the War of the Roses (1455 -1485 ).
1346Battles of Crecy and Neville's Cross; spectacular victories over the French and Scots.
1346 -1348 Black Death devastates Europe.
1360 England and France sign Peace Treaty at Bretigny.
1362 English becomes official language of Parliament and Law Courts. Government secures control of taxation.
1368 Nationalistic revolt overthrows Mongols in China.
1369 100 Years War resumes.
1381 Class struggles and labour shortages leads to Peasants' Revolt led by Wat Tyler.
1385 Scots invade England. Richard II captures Edinburgh.
1388 Scottish army defeat English at Otterburn.
1396 Peace of Paris: 28 year truce between England and France.
1399 Richard II deposed by Henry IV who grants Parliament greater powers.
1400-1413 Owen Glendower leads revolt against English rule in Wales.
1401 De Haerectico Comburendo, burning of heretics made legal.
1415 Battle of Agincourt, Henry V launches conquest of France.
1429 Joan of Arc defeats English at Orleans. Burned at the stake 1431.
1437 Habsburg dynasty takes control of Holy Roman Empire.
1453 French victory over England at Castillion and end of 100 Years War. Byzantium Empire falls to the Turks.
1454 Henry VI goes insane, Duke of York appointed Protector.
1455 -1485 War of the roses. War starts when Duke of York (white rose) revolts against government of Henry VI (red rose).
1476 Caxton sets up press at Westminster.
1478 Start of Inquisition in Spain.
1483 Duke of Gloucester murders Edward V and his brother and proclaims himself King.
1484 Witchcraft declared a heresy by Pope Innocent VIII.
1485 Richard III defeated at Bosworth field by Henry VII (Henry Tudor). End of the War of the Roses.
7- TUDOR ENGLAND
The 16th century saw the conquest of South America by Europe, increased rivalry between France and the Habsburg Empire and the Reformation.
1492 Columbus sails to the New World.
1497 Unification of Spain and end of Moorish rule.
1500 Cabral discovers and claims Brazil for Portugal. Wynkyn de Worde sets up press in Fleet Street.
1510 Slave trading started by Portuguese.
1514 Trinity House founded.
1517 Protestations of Luther starts Reformation marking end of European religious unity.
1519 Start of Habsburg control of Europe by Charles V of France. Cortes begins conquest of Mexico, destroying Aztec civilization.
1519 -1522 Magellan circumnavigates the world.
1521 Luther excommunicated. Protestantism spreads to Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, France and Scotland.
1526 Moslem king, Bábur, captures Delhi founding Mughai dynasty.
1527 Mercenaries sack Rome on orders of Holy Roman Emperor.
1533 Pizarro conquers Peru destroying Inca civilization.
1534 Act of Supremacy: Henry VIII asserts control over English church.
1536 Wales incorporated politically into England by Henry VIII. Dissolution of the monasteries.
1541 Henry VIII declared King of Ireland.
1543 Copernicus forwards heliocentric astronomical theory.
1547 Ivan the Terrible ousts Mongols from Russia.
1551 Threepence introduced.
1555 Mary (Queen of Scots) attempts to introduce Catholicism into Britain. Habsburg Empire split between Spanish and Austrian families.
1559 Church of England re-established by Elizabeth I.
1560 Church of Scotland founded, Calvinism adopted as national religion.
1566 Start of decline of Ottoman Empire after death of Suleiman I (the Magnificent).
1571 Christian League defeats Turkish fleet destroying Moslem sea power in Mediterranean.
1572 Huguenots massacred outside St Bartholomew's on order of catholic French court.
1586 Execution of Mary, Queen of Scots.
1588 Drake defeats Spanish Armada.
1600 British East India Company founded.
8- THE ENGLISH REVOLUTION
An era of absolute monarchies in Europe, especially Louis XIV of France.
1603 Accession of James VI of Scotland as James I of England unites both countries. Widespread plague in Europe.
1603-1668 Togugawa military regime in Japan, isolationist policies and persecution of Christians.
1605 Gunpowder Plot. Catholic plot to blow up Parliament.
1607 Plantation of Ulster with English and Scottish colonists.
1618-1648 Thirty Year's War. Revolt against Catholic Habsburg empire spreads rapidly throughout Europe (last European religious war).
1620 Pilgrim fathers set sail from Plymouth for America.
1625 The Black Death. Charles I moves Parliament from London to Oxford.
1629 Charles I dissolves Parliament for 11 years.
1632 Galileo confirms heliocentric theories of Copernicus (1543).
1638 Torture abolished in England.
1639 -1640 1st and 2nd Bishops' Wars in Scotland.
1641 Irish revolt against English landlords suppressed by Cromwell.
1642-1646 1st Civil War. Charles I and Royalist supporters (Cavaliers) against the Parliamentarians (Roundheads). Cromwell wins decisive battle at Marsden Moor in 1644 . Cavaliers defeated by New Model Army in 1645 . Charles I surrenders in 1646 .
1643 Louis XIV crowned King of France. Establishes Court of Versailles.
1648 2nd Civil War Royalist and Presbyterians crushed by Cromwell.
1649 Charles I beheaded for treason. Cromwell invades Ireland.
1650 Cromwell conquers Scotland.
1651 Battle of Worcester, Cromwell's final victory in England.
1653-1658 Cromwell Lord Protector of Britain.
1660 Restoration of the Monarchy by Charles II.
1663 Turkish war against Holy Roman Empire reaches German border.
1664 Austria defeats Turkish army. England captures Cape Verde Island and wars with Holland. New Amsterdam captured and renamed New York.
1665 The Great Plague.
1666 Great Fire of London.
1670 In secret deal with France, Charles II attempts to restore Catholic power in Britain.
1673 Test Act excludes all Catholics from office.
1677 Princess Mary marries William of Orange.
1678 'Popish Plot', an attempt to restore Catholicism by Titus Oates.
1679 Habeas Corpus Act passed (the right to trial).
1683 Final attempt to bring Islam into Europe by Turks defeated at Vienna.
1688 The Glorious Revolution. Following James II attempts to Catholicise England, Anglicans invite William of Orange to restore Protestant power. Dutch Army lands in November, James II flees to France and the Glorious Revolution is achieved without loss of life.
1689 Powers of the Monarchy devolved to Parliament in the Bill of Rights.
1690 Battle of the Boyne. Aided by Louis XIV, James II leads revolt in Ireland but is defeated by William of Orange.
1694 Bank of England founded.
9- THE 18TH CENTURY
During the 18th century there was a major shift in world power following the War of Austrian succession and the Seven Years' War. France lost most of her colonial gains to Britain and Prussia rose to become the major European power.
1702-1713 War of Spanish Succession. Britain gains control of Gibraltar.
1705 Newcomon invents steam engine.
1707 Act of Union. Scottish Parliament united with England.
1713 Slave trading at its peak.
1715 Jacobite risings against parliamentary union.
1720 Financial Crisis caused by speculation in the 'South Sea Bubble'.
1721 Walpole becomes first Prime Minister.
1733 Kay invents flying shuttle, one of many inventions leading to the industrial revolution.
1740-1748 Austrian War of Succession. Prussia under Frederick now the strongest power in North Europe.
1746 Jacobite risings and massacre at Battle of Culloden, the last battle on British soil. Escape of Bonnie Prince Charlie to Skye.
1752 Gregorian calender adopted in England.
1754 Britain and France war in North America.
1756 Calcutta captured by Nawab of Bengal, 123 British men and women die in 'Black hole of Calcutta'.
1756 -1763 Seven Years' War between Prussia and Austria. Britain declares war against France and joins with Frederick the Great. France and Austria defeated by Prussia and Britain. British colonial gains at their greatest.
1757 Clive defeats Nawab and recaptures Calcutta.
1759 General Wolfe slain capturing Quebec. France surrenders Canadian Territory.
1760 George III challenges Whig oligarchy. Tories remain in power until 1830.
1769 Arkwright erects spinning mill. Cook explores Pacific.
1770 Cook claims Australia for Britain.
1773 Quarrel over taxation between George III and American colonists ends with 'Boston Tea Party'. Stock Exchange founded.
1775 -1783 American War of Independence and formation of the United States of America.
1783 Montgolfier Brothers make the first manned flight in a hot air balloon.
1788 Penal colonies established in Australia.
1789 Washington elected first President of America.
1789 The French Revolution. Bastille stormed July 14 1794 . Republic established by Jacobins.
1795 Napoleon becomes Emperor of France.
1797 The penny, introduced in 8th Century, changes to copper.
1799 Income Tax introduced in England.
10- THE 19TH CENTURY
1801 Parliamentary union between England and Ireland.
1805 Napolean defeats Russian and Austrian armies at Austerlitz. Battle of Trafalgar, Nelsons victory and death on October 21.
1806 Napoleon abolishes Holy Roman Empire.
1812 British seize US ships during blockade of France, invade US and burn Capital and White House. Napoleon attacks Russia but is forced to retreat in 1814 .
1815 Battle of Waterloo, June 18 . Wellington defeats Napoleon.
1821 Grecian revolution against Turks. Napoleon dies.
1823 Spain attempts to regain her American colonies. US declares isolationist policy from Europe.
1825 First railway opens from Stockton to Darlington.
1827 Turkish fleet destroyed at Navarino preventing counter revolution in Greece.
1832 Liberals (Whigs and industrialists) carry through Reform Bill transferring political power from aristocracy to middle classes.
1833 Slaves liberated throughout British Empire.
1834 Tolpuddle Martyrs transported to Australia for forming a trade union. Slave trading abolished in Britain.
1836 Boers set up a republic in Transvaal after escaping from British rule in the Cape.
1838 Chartism flourishes. British Democratic Movement, formed mainly from working classes, demands to be included in Liberal franchise of 1832.
1839 -1842 and 1856 -1858 Opium wars between Britain and China.
1840 Penny post introduced. Great Irish potato famine leads to mass emigrations.
1841 Britain acquires Hong Kong.
1846 Repeal of Corn Laws.
1848 Year of unrest throughout Europe.
1849 Livingstone explores interior of Africa.
1851 Great Exhibition in London.
1853-1856 Crimean War. Russian ambitions towards India result in alliance of Britain and France declaring war on Russia. Turkey and Sardinia join the allies, Russia withdraws from Sebastopol.
1857 Indian Mutiny crushed by British government.
1860-1865 American civil War.
1863 Underground railway opens in London.
1864 Peasants Revolt in China brutally suppressed by western forces.
1866 Austro-Prussian War reduces power of Habsburg Empire.
1867 Last convicts transported to Australia. Formation of Dominion of Canada.
1869 Suez Canal opens. US Trans-continental railway completed.
1870-1871 Napoleon III loses Franco-Prussian war and empire collapses. Germany unified under Prussian Kaiser.
1872 Secret Ballot introduced in Britain.
1875 Britain buys control of Suez Canal. Captain Webb swims English Channel.
1876 Alexander Graham Bell invents telephone.
1878 Bulgaria separates from Turkey. Britain gains control of Cyprus.
1882 Britain occupies Egypt and is drawn into holy war with Sudan.
1884 GMT (Standard Time) adopted worldwide.
1889 Great London dock strike August 15 - September 16 .
1893 Rejection of Irish Home Rule Bill by parliament.
1894 Manchester Ship Canal completed
1899 -1902 Boer War. Conflict in Transvaal over mining rights. Mafeking and Ladysmith relieved in 1900.
11- THE 20TH CENTURY
1900 Boxer rising fails (revolt over European and Japanese interference in China), collapse of Imperial rule. Count Zeppelin builds the first dirigible. Formation of Labour Party.
1901 Foundation of Commonwealth of Australia.
1903 Wright brothers make first heavier-than-air flight. Henry Ford introduces production line car manufacturing.
1904 -1905 Completion of the Trans-Siberian Railway. Russia moves into Manchuria and Korea but is defeated by Japan.
1909 Louis Bleriot flies across the channel.
1911-1912 Chinese Revolution. Nationalists overthrow Imperialist regime.
1912 Sinking of the Titanic.
1914 Panama Canal opens.
1914-1918 First World War begins following assassination of Archduke Ferdinand in Sarajevo on 28 Jun. Germans sign Armistice Nov 11th 1918 .
1917 Bolshevik Revolution in Russia.
1918 End of Habsburg Empire as Austria and Hungary are separated.
1919 Treaty of Versailles. Formation of Polish Republic, Yugoslavia and Czechoslovakia. Ottoman empire breaks up. League of Nations formed. Alcock and Brown fly across the Atlantic.
1921 Ireland split into Irish Free State and Ulster.
1922 Mussolini establishes fascism in Italy.
1924 Lenin dies and Stalin takes control of the new communist regime. First Labour government.
1926 General Strike.
1927 Charles Lindenburgh flies solo across the Atlantic. Airship Graf Zeppelin circumnavigates the globe.
1929 World wide economic crises plunges many industrial countries into recession.
1931 Spanish monarchy collapses and republic formed. Japan invades China and resigns from League of Nations.
1933 Hitler Chancellor of Germany.
1935 Hitler denounces Treaty of Versailles which limits size of German armed forces. Italy invades Ethiopia.
1936 Plaid Cymru (Welsh Nationalist Party) founded.
1936 -1939 Spanish Civil War and start of General Franco's Fascist dictatorship.
1937 Irish Free State becomes Republic of Ireland.
1938 Germany unites with Austria. Sudentenland in Czechoslovakia returned to Germany. Forcible suppression of Jews.
1939 -1945 Second World War. War begins after Hitler invades Czechoslovakia and Poland. End of the Second World War against Germany declared at 1 minute past midnight on 8th May. Japan surrenders on 2nd Sep after atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
1944 Civil war in Greece.
1945 United Nations formed. First Scottish Nationalist MP elected.
1946 -1949 Chinese civil war. Nationalist government replaced by communists under Mao Tse-Tung.
1947 Russia boycotts economic assistance for Europe (The Marshall Plan). Charles Yeager breaks the sound barrier.
1948 National Health Service introduced. Communist takeover of Czechoslovakia, an 'iron curtain' raised across Europe. Proclamation of State of Israel.
1949 Formation of NATO. The Berlin airlift. DeHavilland Comet enters service. China invades Taiwan.
1950 China invades Tibet.
1950-1953 Invasion of South Korea by communist North Korea, UN forces come to aid of South Korea.
1951 King Farouk of Egypt forced to abdicate. Festival of Britain.
1953 Edmund Hilary and Sherpa Tensing reach summit of Everest.
1954 End of French rule in Indo-China, independence for Laos, Cambodia and S Vietnam. Communist take control in North Vietnam.
1956 Uprising in Hungary suppressed by Soviet tanks. Nasser seizes Suez Canal, Israel invades Egypt, France and Britain land in Port Said.
1957 Formation of the EEC. Sputnik I launched.
1958 Civil war in France averted by de Gaulle's return to power.
1959 Fidel Castro ends Bastida regime in Cuba. Dali Llama flees Tibet for LA.
1959 -1975 Second Indo-China War, North Vietnam and Viet-Cong against South Vietnam.
1960 Independence and then chaos for Congo, UN intervenes to help. Start of 27 year civil war in Chad.
1961 Major Yuri Gagarin is first man in space. Berlin Wall built. Army and extremists attempt coup in Algeria.
1962 Cease fire and Independence in Algeria. Crisis as Kennedy demands removal of Soviet nuclear missiles from Cuba.
1963 End of conflict in Congo. USA, Britain and Russia sign Test Ban Treaty. JFK assassinated.
1965 Churchill Dies. India and Pakistan fight over Kashmir. America enters Indo-China War.
1966 Mrs Ghandi becomes India's first woman Prime Minister. Military coups in Ghana and Nigeria.
1967 Military Junta takes control in Greece. Six Day War, Israel defeats Egyptian, Jordanian and Syrian armed forces. Civil War in Nigeria.
1968 Russia invades Czechoslovakia. Martin Luther King and Robert Kennedy assassinated.
1969 Start of American withdrawal from Vietnam. Armstrong and Aldrin walk on the moon. Woodstock festival. General de Gaulle retires. British troops move into Northern Ireland. First flights of Concorde, Boeing 747 Jumbo and Harrier jump jet.
1970 Voting age lowered from 21 to 18 . End of Nigerian Civil War. 43 countries sign treaty limiting nuclear weapons. Military coup in Cambodia.
1971 Coup in Uganda, Idi Amin declared new leader. Decimal system of coinage adopted in UK. Internment introduced in NI.
1972 Palestinian terrorists attack Israeli Olympic team in Munich. President Amin expels Asians from Uganda. 'Bloody Sunday': troops fire on Catholic demonstrators in NI.
1973 Cease-fire in Vietnam. Egypt and Syria invade Israel during Yom Kippur. Oil embargo against pro-Israeli countries. Coup in Chile by General Pinochet.
1974 Miners strike forces three day week. Referendum over devolution for Scotland and Wales. Nixon resigns over Watergate bugging scandal. Turkey invades Cyprus. Coup in Portugal. Emperor Haile Selassie deposed in Ethiopia.
1975 UK joins EC. Israeli commandos raid hi-jacked aircraft at Entebbe. Civil wars in Lebanon and Mozambique. King Feisal of Saudi Arabia assassinated. Suez Canal re-opens. N.Vietnamese communists capture Saigon (now Ho Chi Minh City), Pathet Lao control Laos. Khmer Rouge defeat military government, Pol Pot begins reign of terror in Cambodia. North Sea oil production starts.
1976 Concorde starts regular service. Viking I and II land on Mars. Mao Tse-tung dies. Syrian army imposes truce in Lebanon. Harold Wilson resigns; Britain goes to IMF. Cod War over fishing rights between Britain and Iceland. Start of civil war in Angola. Heatwaves and drought across much of England and Wales.
1977 Baader-Meinhof Group hijack aircraft in Germany. First free elections in Spain since civil war. SA activist Steve Biko dies in jail. Aerospace and shipbuilding privatised. Space Shuttle makes first free flight.
1978 First 'test tube baby', Louise Brown, is born. Vietnam invades Cambodia overthrowing Khmer Rouge. End of Pinochet regime in Chile.
1979 Shah deposed in Iran, Ayatollah Khomeni sets up Islamic Republic. Peace treaty signed ending 30-year Israeli-Egyptian war. Tanzania invades Uganda, Amin flees. European Parliament's first session in Strasbourg. US Embassy held by students in Teheran. Wildcat strikes in the 'Winter of Discontent'. Conservatives under Margaret Thatcher overwhelm Labour. Soviet Union invades Afghanistan. Man powered 'Gossamer Albatross' crosses the channel.
1980 SAS rescue hostages held in Iranian Embassy. Strikers in Gdansk granted permission to form trade union. Iran and Iraq war over border and territorial rights.
1981 Reagan elected president, American hostages in Teheran released. SDP formed. Rioting in major cities in Britain. President Sadat of Egypt assassinated. Martial law declared in Poland after nationwide strikes. Space Shuttle 'Columbia' lands after 54 hours in space.
1982 Falklands War. Israel invades Lebanon. Flagship of Henry VII, the Mary Rose, raised in Portsmouth. Thames barrier completed. Frontier between Spain and Gibraltar opened.
1983 Suicide driver blasts American Embassy in Beirut. Revolutionary council in Grenada ousted by American troops. Argentina elects civilian government. Start of civil war in Sudan. Brinks Matt bullion robbery.
1984 Miners strike over pit closures. WPC Yvonne Fletcher shot outside Libyan People's Bureau. Famine in Ethiopia. Chemical plant explodes in Bhopal, India. IRA bomb Brighton Hotel during Tory Conference. Indira Gandhi assassinated by Sikh Bodyguards. British Telecom privatized.
1985 House of Lords televised. French secret service sink Greenpeace ship 'Rainbow Warrior' in NZ. Famine relief concert (Band Aid) organised by Bob Geldof. Wreck of the Titanic found. Anglo-Irish agreement signed in Dublin.
1986 Challenger space shuttle explodes on take-off. President Marcos exiled from Philippines by Corazon Aquino. US bomb Tripoli following Libyan terrorist acts in Europe. Nuclear disaster at Chernobyl spreads radioactive cloud over much of Europe. Voyager aircraft circles globe without refuelling.
1987 Soviet policy of glasnost (openness) begins. British Airways privatised. 'Herald of Free Enterprise' capsizes outside Zeebrugge. Syrian troops enter Beirut on behalf of Lebanese government. Cease fire in Chad (after 27 years). Military coup in Nigeria. Stock market crashes. 'Irangate' arms for hostages scandal in Washington. 30 die in Kings Cross fire. 'Virgin Atlantic Flyer' hot-air balloon crosses the Atlantic.
1988 Comic Relief. House of Commons televised. Hurricane in UK. SAS shoot 3 IRA terrorists in Gibraltar. Clapham rail disaster. Piper Alpha oil rig explodes killing 167 workers. Pan Am jumbo explodes over Lockerbie.
1989 Soviet withdraw from Afghanistan. Exxon Valdez hits reef in Alaska spilling 10 million gallons of oil. Poll Tax introduced in Scotland. Tiananmen Square massacre in China. Ayatollah Khomeni dies. Water companies privatized. US invade Panama. Berlin Wall falls. Peaceful revolutions in most of eastern Europe.
1990 Poll Tax introduced in England and Wales. Riot at Strangways prison, prisoners hold rooftop siege. Nelson Mandela released. End of the Cold War, Warsaw Pact disbands. Iraq invades Kuwait. Britain joins European exchange rate mechanism. East and West Germany unified after 40 years. Margaret Thatcher resigns. Electricity companies privatised.
1991 Iraqi troops ousted from Kuwait by allied forces, Kurdish rebellion crushed by Hussein. Virgin Pacific Flyer hot-air balloon crosses Pacific. Famine and end to 30 year civil war in Ethiopia. Start of civil war in Somalia. Indian PM Rajiv Gandhi assassinated by suicide bomber. Civil war in Yugoslavia. Recession in UK and many other countries. Treaty of Europe signed at Maastricht. Communist party collapses, USSR replaced by Commonwealth of Independent States.
1992 Famine in Somalia. War in Bosnia-Herzegovina between ethnic Croatians, Serbians and Muslims. UN troops enter Somalia and BH to protect food aid. End of civil wars in Mozambique and Somalia. Riots in Los Angeles. Last hostages released in Lebanon. Mujhadeen take control in Afghanistan, start of civil war. Czechoslovakia splits into the Czech Republic and Slovakia. Black Wednesday (September 16th), speculators force Britain and Italy to pull out of the ERM. Church of England endorses ordination of women. Mount Etna erupts. Fire at Windsor Castle.
1993 MV Braer runs aground on Shetland Islands. Sir Ranaulph Fiennes crosses the Antarctic on foot. Solicitors granted permission by Lord Chancellor to act in the Higher Courts. Queen and Prince Charles start paying income tax. James Bulger murdered by two boys. End of recession. ERM collapses. Russian hardliners seize White house. Siege in Waco, Texas, ends as fireball kills all members of Dravidian Sect. USA, Canada and Mexico form NAFTA. Overladen Haitian ferry capsizes killing 2000. Civil war and famine in Sudan. End of 30 year civil war in Angola. Monarchy restored in Cambodia.
1994 Nelson Mandela president of SA after first ever free elections. GATT signed by 120 countries. Israel hands over Gaza to Palestinians Civil war in Rwanda, massacre of 700 000 by government troops. Comet Schumaker-Levy hits Jupiter. US ousts General Cedras from Haiti. Israel and Jordan sign peace treaty ending 46 years of war. Russian troops invade breakaway Republic of Chechnya. Oil pipeline bursts in N. Russia. End of war between Croatia and Serbia. Estonian ferry capsizes in Baltic killing 900. 53 members of Order of Solar Temple cult die in suicide pact. Eurostar begins passenger services through channel tunnel. IRA and loyalist terrorists renounce violence ending 25 year conflict in which 3172 have died. National Lottery launched.
1995 Earthquake in Kobe, Japan, kills 5000. SAREN nerve agent released into Tokyo underground by Omm religious sect. Right wing extremists bomb Government building in Oklahoma City: 200 dead. Ebola virus in Kenya: 200 dead. Earthquake in Russia: 2000 dead as 17 tower blocks collapse. Rugby Union turns professional. Nick Leeson leaves Barings bank with £860m of dept. France carries out nuclear tests in Pacific in defiance of Test Treaty ban. Fire in Baku underground: 300 dead. Drought in UK. Nigeria hangs 9 human rights protesters. Rosemary West sentenced for 9 murders. Troops leave the streets of NI. Israeli PM, Itzhak Rabin, assassinated by student. West Bank settlements handed to Palestinians. BH peace deal agreed in Dayton Ohio, 60000 NATO troops to enforce settlement.
1996 Mitterand dies. Arafat wins Palestinian presidential elections. IRA break cease fire - bombs at Canary Wharf, Arndale Centre and Army HQ in NI. Dunblaine - Thomas Hamilton kills 16 at primary school. Worldwide beef ban follows BSE scare. Tasmania, gunman kills 34 on shooting attack. ESA Ariane V rocket destroyed on take-off. Evidence of bacterial life found on Mars. Cease fire in Chechnya. Extreme Islamic law declared in Afghanistan. Volcanic Eruption under Vatnajökull glacier in Iceland followed by severe flooding. 2 million Rwandan refugees return home from Zaire. Fire in Channel Tunnel. Lorry drivers strike paralyses France - border crossings closed. Peru, hostage crisis in Japanese Embassy.
1997 Demonstration in Albania over collapse of pyramid selling organisations. Labour win landslide victory - 171 majority. NASA rover explores Mars. Accident on Mir space station results in power loss and air leaks. End of civil war in Zäire, renamed Democratic Republic of Congo. NATO and Russia sign joint agreement. Coup in Sierra Leone. Hong Kong handed over to China. Volcano devastates Monseraat. Princess Diana dies after car crash in Paris. Smog blanket over SE Asia from forest fires in Indonesia. Scotland and Wales vote yes to devolution. Thrust II jet car breaks sound barrier. Windsor castle opens after rebuilding. Terrorist attack at Luxor - 58 killed. Britannia decommissioned after 44 years.
1998 20m tall Angel of the North unveiled. Countryside protest in London. floods in England. Good Friday peace agreement signed in NI. Pol Pot dies. Train crash in Germany kills over 100. France98 : British fans rampage in Marseilles. Drug allegations disrupt Tour de France. Omagh bomb kills 28 and injures 200. Clinton indited of perjury over Lewinsky affair. Viagra impotency drug comes on the market.